- A+
- mustache语法
- v-once语法
- v-html
- v-cloak
- v-pre
- v-text
- v-bind的基本使用
- v-bind动态绑定的class
- v-bind动态绑定style
- 基本使用
- 计算属性的getter和setter
- 计算属性和methods
- 复杂操作
- v-on的基本使用
- v-on的参数传递
- v-on的修饰符
- v-if
- v-show
- v-for遍历数组元素
- v-for 访问对象
- 在使用v-for时尽量配合key使用
- 数组更新
- v-model的基本使用
- v-model结合checkbox
- v-model结合radio
- 创建组件构造器
- 注册组件
- 使用组件
- 什么是npm:
- cnpm的安装
- 安装vue脚手架
- 同时使用cli3和cli2方法:
- vue cli2
- vue cli3
- 搭建步骤
- 使用vue-rounter的步骤
- 路由的默认路径
- 默认的hash模式,改为history模式,在index.js文件中修改
- rounter-link属性问题
- 动态路由
- 路由的懒加载
- 什么是嵌套路由?
- 实现步骤:
- 参数传递的方式:params和query
- $rounter 和 rounte的区别
- 什么是导航守卫?
- 使用:
- 基本使用:
- 参数和传入对象
- 主要包括两部分:
- 在通过mutation更新数据的时候,希望携带的额外的参数被称为mutation的载荷(PayLoad)
- 提交风格
- 响应规则
- 常量类型
- 同步函数
- 多种请求方式
- 发送并发请求
- 全局配置
- axios实例
Vue学习笔记
认识vue
渐进式框架,什么是渐进式?
渐进式意味着你可以将vue作为你应用的一部分嵌入其中
vue特点
解耦视图和数据
可复用的组件
前端路由技术
状态管理
虚拟DOM
安装
响应式开发
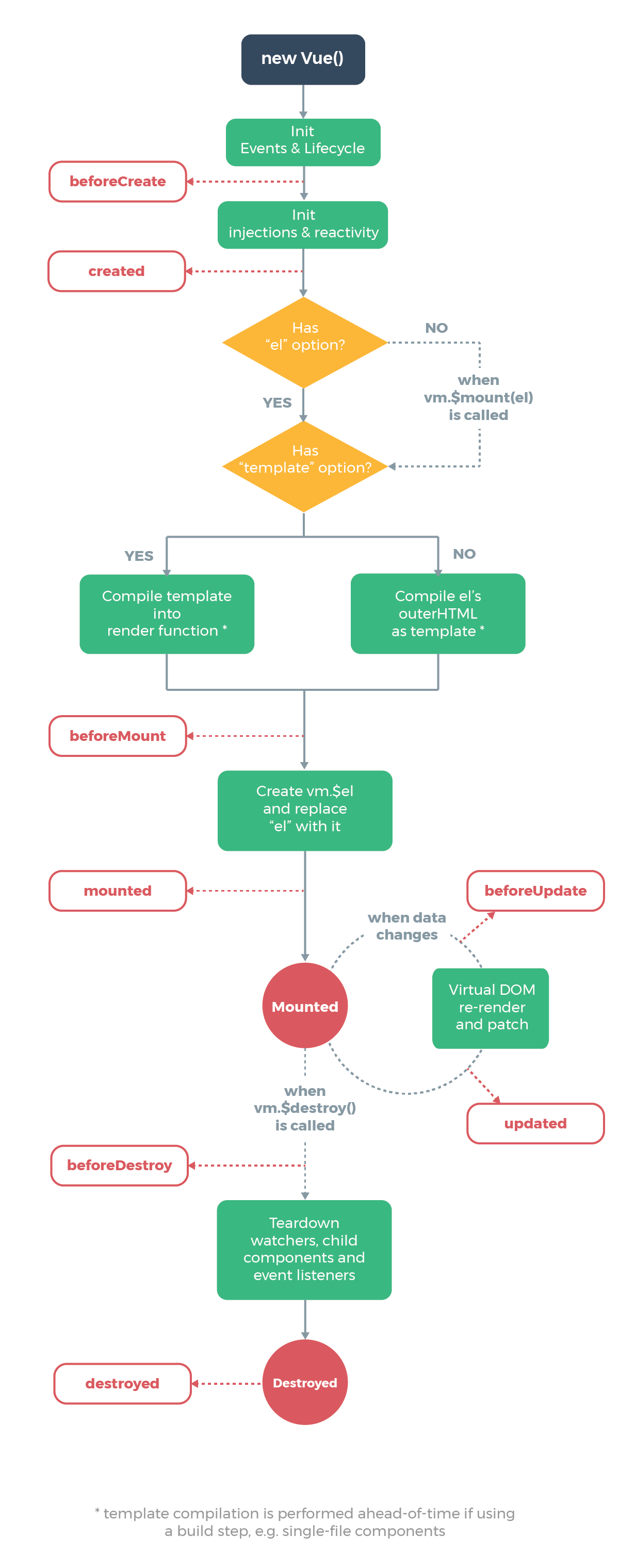
生命周期
webstorm 模板功能
基础知识
插值操作
mustache语法
<span>Message: {{ msg }}</span> v-once语法
<span v-once>这个将不会改变: {{ msg }}</span> v-html
<div id="app"> {{message}} <h2 v-html="url"></h2> </div> <script src="/js/vue.js"></script> <script> let app = new Vuae({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello", url:'<a href="www.baidu.com">百度一下</a>' } }) </script> v-cloak
作用:在vue解析之前,div中有一个属性v-cloak;
在vue解析之后,div中没有属性v-cloak
<style> [v-cloak]{ display: none; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app" v-cloak> <h2>{{message}}</h2> <h2></h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> setTimeout(function(){ let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello" } }) },1000) </script> v-pre
<div id="app"> <h2>{{message}}</h2> <h2 v-pre> {{message}}</h2> #不做解析,原封不动 </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello" } }) </script> v-text
<div id="app"> {{message}} <h2 v-text="message">,hello</h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello" } }) </script> 绑定属性
v-bind的基本使用
<div id="app"> <h2>{{message}}</h2> <h2></h2> <img v-bind:src="imgurl" alt=""> <!-- v-bind语法糖,即简写方式--> <!-- <img :src="imgurl" alt="">--> </div> v-bind动态绑定的class
<style> .active{ color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h2 :class="active">{{message}}</h2> <!-- 对象语法--> <!-- <h2 v-bind:class="{key1:vlue1,key2:value2}"></h2>--> <!-- <h2 v-bind:class="{类名1: true , 类名2: boolean}"></h2>--> <!-- 可以同时加载原始的class,两个之间会自动合并--> <h2 v-bind:class="{active: isActive , line: isLine}" class="title">{{message}}</h2> <h2 v-bind:class="getClasses()" class="title">{{message}}</h2> <button v-on:click="btnClick">按钮</button> <!-- 数组语法--> <h2 :class="['active','line']" class="title"></h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello", active:'active', isActive:true, isLine:true }, methods:{ btnClick:function (){ this.isActive = !this.isActive }, getClasses:function(){ return {active: this.isActive , line: this.isLine} } } }) </script> v-bind动态绑定style
绑定方式一:对象语法
:style="{color:currentColor, fontSize:fontSize + 'px'}" 计算属性
基本使用
computed:{ fullName:function (){ return this.firstname + ' ' + this.lastname } 计算属性的getter和setter
<script> let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ firstname:'小明', lastname:'王' }, //计算属性一般是没有set方法,只读属性 computed:{ //简便写法 // fullName:function (){ // return this.firstname + ' ' + this.lastname // } //原始属性 fullName:{ set:function (newvalue){ const name = newvalue.split(' '); this.firstname = name[0]; this.lastname = name[1]; }, get:function (){ return this.firstname + ' ' + this.lastname } } } }) </script> 计算属性和methods
<div id="app"> <!-- 方法一 直接拼装 : 语法过于繁琐--> <h2>{{firstname}} {{lastname}}</h2> <!-- 方法二 通过定义methods,需要多次使用时,需要多次调用--> <h2>{{getfullName()}}</h2> <!-- 方法三 通过computed,多次调用时,可以实现缓存,只调用一次,更高效--> <h2>{{fullName}}</h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ firstname:'小明', lastname:'王' }, computed:{ fullName:function (){ return this.firstname + ' ' + this.lastname } }, methods:{ getfullName(){ return this.firstname + ' ' + this.lastname } } }) </script> 复杂操作
<div id="app"> <h2>总价格:{{totalPrice}}</h2> <h2></h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ books:[ {id: 110, name: 'python编程', price: 120}, {id: 112, name: 'c编程', price: 120}, ] }, computed:{ totalPrice:function (){ let total = 0 for (let i in this.books){ total += this.books[i].price } return total } } }) </script> 事件监听
v-on的基本使用
<div id="app"> <h2>{{counter}}</h2> <button v-on:click="increment">+</button> <button v-on:click="decrement">-</button> <!-- 语法糖写法--> <!-- <button @click="increment"></button>--> <h2></h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ counter:0 }, methods:{ increment(){ this.counter++ }, decrement(){ this.counter-- } } }) </script> v-on的参数传递
<div id="app"> <!-- 调用方法没有参数--> <button @click="btnclick1">按钮1</button> <button @click="btnclick1()">按钮1</button> <!-- 在事件定义时,写函数时省略了小括号,但是方法本身需要一个参数--> <!-- 如果函数需要参数,但是没有传入,那么函数的形参为undefined--> <button @click="btnclick2(123)">按钮2</button> <button @click="btnclick2()">按钮2</button> <!-- vue会默认将浏览器生产的event事件对象做作为参数传入到方法--> <button @click="btnclick2">按钮2</button> <!--方法定义时,需要event对象,又需要其他参数--> <!-- 手动获取浏览器参数的event对象: $event --> <button @click="btnclick3(123, $event)">按钮3</button> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello" }, methods:{ btnclick1(){ console.log("btnclick1") }, btnclick2(abc){ console.log("------",abc) }, btnclick3(abc, event){ console.log("+++", abc, event) } } }) </script> v-on的修饰符
<div id="app" @click="divclick"> <!-- .stop修饰符: 阻止事件冒泡--> <button @click.stop="btnclick">按钮</button> </div> <br> <!-- .prevent修饰符: 阻止默认事件--> <form action="baidu"> <input type="submit" value="提交" @click.prevent="submitclick"> </form> <!-- 监听键盘某个键--> <input type="text" @keyup.enter="keyup"> <!--v-once--> 条件渲染
v-if
v-if和v-else
<div id="app" > <h2 v-if="isShow"> <div>{{message}}</div> </h2> <h1 v-else>isShow为false时,显示我</h1> <h2></h2> </div> v-else-if
<div v-if="type === 'A'"> A </div> <div v-else-if="type === 'B'"> B </div> <div v-else-if="type === 'C'"> C </div> <div v-else> Not A/B/C </div> key的使用和案例
<div id="app"> <span v-if="showCount"> <label for="username">账号:</label> //for的作用,关联标签 <input type="text" placeholder="请输入账号" id="username" key="user"> </span> <span v-else> <label >邮箱:</label> <input type="text" placeholder="请输入邮箱" key="email"> </span> <button type="submit" @click="change" >切换类型</button> </div> <!--key 的作用,解决输入文本框中文字时,vue渲染时出现共用相同的输入框--> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello", showCount:true }, methods:{ change(){ return this.showCount = !this.showCount } } }) </script> v-show
<div id="app"> <h2 v-if="isShow">{{message}}</h2> <!-- v-show的值为false时,v-show只是给元素添加一个行内样式display:none--> <h2 v-show="isShow">{{message}}</h2> </div> 列表渲染(循环遍历)
v-for遍历数组元素
<ul id="example-1"> <li v-for="item in items" :key="item.message"> {{ item.message }} </li> </ul> //同时支持访问第二参数,即当前项的索引 <ul id="example-2"> <li v-for="(item, index) in items"> {{ parentMessage }} - {{ index }} - {{ item.message }} </li> </ul> v-for 访问对象
<ul id="v-for-object" class="demo"> <li v-for="value in object"> {{ value }} </li> </ul> //同时支持第二,第三参数 <div v-for="(value, name, index) in object"> {{ index }}. {{ name }}: {{ value }} </div> <script> new Vue({ el: '#v-for-object', data: { object: { title: 'How to do lists in Vue', author: 'Jane Doe', publishedAt: '2016-04-10' } } }) </script> 在使用v-for时尽量配合key使用
作用:为了更高效的更新虚拟DOM
数组更新
push() pop() shift() unshift() splice() sort() reverse() 表单数据绑定v-model
v-model的基本使用
<div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model="message"> <h2>{{message}}</h2> <h2></h2> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello" } }) </script> v-model结合checkbox
<div id="app"> <input type="checkbox" id="agree" v-model="isAgree">同意协议 <label for="agree"></label> <h2>同意协议:{{isAgree}}</h2> <button :disabled="!isAgree">下一步</button> <br> <input type="checkbox" id="jack" value="jack" v-model="checked">jack <label for="jack"></label> <input type="checkbox" id="joy" value="joy" v-model="checked">joy <label for="joy"></label> <h3>chengbox:{{checked}}</h3> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello", isAgree:false, checked:[] } }) </script> v-model结合radio
<div id="app"> <label for="male"> <input type="radio" id="male" v-model="sex" value="男"> 男 </label> <label for="female"> <input type="radio" id="female" v-model="sex" value="女">女 </label> <h2>选择的性别:{{sex}}</h2> <!-- <label for="male">--> <!-- <input type="radio" id="male" name="sex" v-model="sex" value="男"> 男--> <!-- </label>--> <!-- <label for="female">--> <!-- <input type="radio" id="female" name="sex" v-model="sex" value="女">女--> <!-- </label>--> <!-- <h2>选择的性别:{{sex}}</h2>--> </div> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello", sex:'男' } }) </script> 组件化开发
注册组件的步骤
-
创建组件构造器
-
注册组件
-
使用组件
-
调用Vue.extend()方法 创建组件构造器
-
调用Vue.conponent()方法 注册组件
-
在vue实例的作用域中使用组件
-
组件化的基本使用
<div id="app"> <!-- //3、使用组件--> <my-cpn></my-cpn> </div> <script> //1、创建组件构造器 //tab键上方的点可以用来定义字符串,可以换行定义 const cpnC = Vue.extend({ template:` <div> <h2>我是标题</h2> </div> ` }) //2、注册组件 Vue.component('my-cpn',cpnC) let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello" } }) </script> 全局组件和局部组件
//注册组件(全局组件) Vue.component('cpn',cpnC) let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello" }, //注册局部组件 components:{ //cpn使用组件的标签名 cpn:cpnC } }) let app2 = new Vue({ el:'#app2', data:{ message:"hello" } }) 父组件和子组件
//创建第一个组件构造器 const cpnC1 = Vue.extend({ template:` <div> <h2>我是标题1</h2> </div> `, }) //创建第二个组件构造器 const cpnC2 = Vue.extend({ template:` <div> <h2>我是标题2</h2> <cpn1></cpn1> </div> `, components:{ cpn1: cpnC1 } }) let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello" }, components:{ // cpn1: cpnC1, cpn2: cpnC2 } }) 组件的语法糖写法
<script> //语法糖写法,注册全局组件 Vue.component('cpn1',{ template:` <div> <h2>我是标题1</h2> </div>` }) let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello" }, //注册局部组件 components:{ 'cpn2':{ template:` <div> <h2>我是标题2</h2> </div> ` } } }) </script> 组件模板分离写法
<!--方法一 --> <!--<script type="text/x-template" id="cpn">--> <!-- <div>--> <!-- <h2>我是标题1</h2>--> <!-- </div>--> <!--</script>--> 方法二,tempalte标签 <template id="cpn"> <div> <h2>我是标题</h2> </div> </template> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.component('cpn',{ template:'#cpn' }) let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello" } }) </script> 组件的数据存放
Vue.component('cpn',{ template:'#cpn', //每个组件都是独立的实例对象,如果data不是一个函数,在组件复用的时候会出现数据不能独立的情况 data(){ return { counter:0 } }, methods:{ increment(){ this.counter++ }, decrement(){ this.counter-- } } }) 组件通信-父传子
<div id="app"> <cpn v-bind:cmovies="movies" :cmessage="message"> </cpn> </div> <template id="cpn"> <div> <h2>{{cmovies}}</h2> <div>{{cmessage}}</div> </div> </template> <script src="../js/vue.js"></script> <script> const cpn = { template:`#cpn`, // props:['cmovies','cmessage'] props:{ // 1、类型限制 // cmovies:Array, // cmessage:String, //提供一些默认值,以及必传值 cmessage:{ type:String, default:'aaaaa', //表示该值为必须传入 required:true }, //类型是对象或者数组时,默认值必须是一个函数 cmovies:{ type:Array, dafault(){ return [] } } } } let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello", movies:['海贼王','海尔兄弟'] }, components:{ cpn } }) </script> 组件通信-子传父
<!--父组件模板--> <div id="app"> <cpn @itemclick="cpnClick"></cpn> </div> <!--子组件模板--> <template id="cpn"> <div> <button v-for="item in categories" @click="btnClick(item)"> {{item.name}} </button> </div> </template> <script> //子组件 const cpn = { template:`#cpn`, data(){ return { categories:[ {id: 'aaa', name: '热门推荐'}, {id: 'bbb', name: '手机数码'}, {id: 'ccc', name: '数码家电'} ] } }, methods:{ btnClick(item){ //发射事件('自定事件的名字', 参数) this.$emit('itemclick', item) } } } //父组件 let app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ message:"hello" }, components:{ cpn }, methods:{ cpnClick(item){ console.log('cpnclick', item) } } }) </script> Vue CLI
使用前提
什么是npm:
全称:Node Package Manager
包管理工具
cnpm的安装
原因:国内访问npm官方镜像比较慢
淘宝npm镜像安装:
npm install -g cnpm -- register=http://register.npm.taobao.org
使用方法:
cnpm install [包name]
vue cli的使用
安装vue脚手架
npm install -g @vue/cli
同时使用cli3和cli2方法:
npm install -g @vue/cli-init
vue cli2
初始化项目
vue init webpack my-project
runtime-only 和 runtime-compiler的区别:
- runtime-compiler:
- template ->ast(抽象语法树)->render->vdom-ui
- runtime-only:
- render-vdom UI
- 下面的性能更好,代码量更少
vue cli3
初始化项目
vue create my-project
vue-rounter
改变URL不刷新界面的方式
- location.hash = 'xxx'
- HTML的history模式:
- pushState: history.pushState({}, '', 'home') 压入栈
- history.back:
- replaceState: history.replaceState({}, '', 'home') 替换
- go : history.go(number)
使用vue-rounter
- 导入路由对象,并且调用vue.use(vuerounter)
- 创建路由实例,并且传入路由映射配置
- 在vue实例中挂载创建的路由实例
vue-rounter的基本使用
搭建步骤
在src文件夹目录下创建rounter目录,然后创建index.js文件,配置如下
配置路由相关的信息 import VueRouter from 'vue-router' import Vue from 'vue' //1. 通过vue.use(插件), 安装插件 Vue.use(VueRouter) //2. 创建VueRouter对象 const routes = [ ] const router = new VueRouter({ //配置路由和组件之间的应用关系 routes }) //3. 将router对象传入到Vue实例中 export default router 使用vue-rounter的步骤
- 创建路由组件
- 配置路由映射:组件和路径的映射关系
- 使用路由:通过
和
路由的默认路径
const routes = { path: '', redirect: '/home' } 默认的hash模式,改为history模式,在index.js文件中修改
const router = new VueRouter({ //配置路由和组件之间的应用关系 routes, // 默认路由方式为hash,一下修改为h5的history模式 mode: 'history' }) rounter-link属性问题
- tag:tag可以指定
之后渲染成什么组件,比如:tag='li' - replace:replace不会留下history记录,所以指定replace的情况下,后退键返回不能返回到上一个界面中
- LinkActiveCalss:当
对应的路由匹配成功时,会自动给当前元素设置一个rounter-link-active的class,设置LinkActiveClass可以修改默认的名称
动态路由
- 添加相关组件,创建组件如User组件
- 在index.js文件中添加该组件信息
- 在App.vue中使用该组件动态路由
路由的懒加载
路由懒加载的作用
主要作用就是将路由对应的组件打包成一个个的js代码块;
只有在这个路由被访问到的时候,才加载对应的组件
路由懒加载的方式
-
结合vue的异步组件和webpack的代码
-
AMD写法:
const About = resolve => require(['../components/About.vue],resolve) -
ES6中,更加简单的写法来组织vue异步组件和webpack的代码分割
const Home = () => import ('../components/Home.vue)
vue-rounter的嵌套路由
什么是嵌套路由?
- 比如在Home页面中,我们希望通过/home/news 和 /home/message访问一些内容
- 一个路径映射一个组件,访问这两个组件也会分别渲染两个组件
实现步骤:
- 创建对应的子组件,并且在路由映射中配置对应的子路由
- 在组件内部使用
标签
vue-rounter参数传递
参数传递的方式:params和query
params的类型
- 配置路由格式: /router/:id
- 传递的方式: 在path后面跟上对应的值
- 传递后形成的路径:/router/123, /router/abc
query类型
- 配置路由格式:/router, 也就是普通格式
- 传递方式:对象中使用query的key作为传递方式
- 传递后形成的路径: /router?id=123, /router?id=abc
$rounter 和 rounte的区别
- router: router是VueRouter的一个对象,通过Vue.use(VueRouter)和VueRouter构造函数得到一个router的实例对象,这个对象中是一个全局的对象,他包含了所有的路由包含了许多关键的对象和属性
- **route: **route是一个跳转的路由对象,每一个路由都会有一个route对象,是一个局部的对象,可以获取对应的name,path,params,query等
vue-rounter导航守卫
什么是导航守卫?
- vue-router提供的导航守卫主要用来监听监听路由的进入和离开
- vue-router 提供了beforeEach和afterEach的钩子函数,他们会在路由即将改变前和改变后触发
使用:
分类:
- 全局守卫
- 路由独享的守卫
- 组件内的守卫
参数:
- to: 即将要进入的目标的路由信息
- from: 当前导航即将要离开的路由对象
- next: 调用该方法,才能进入下一钩子
tips:
如果是后置钩子,也就是afterEach, 不需要主动去调用next()函数
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => { //从from跳转到to document.title = to.matched[0].meta.title next() }) keep-alive
-
keep-alive是vue内置的一个组件,可以使被包含的组件保留状态,或避免重新渲染
两个重要属性:
include - 字符串或正则表达式,只有匹配的组件会被缓存
exclude - 字符串或者正则表达式,任何匹配的组件都不会被缓存
-
rounter-view也是一个组件,如果直接被包在keep-alive里面,所有路径匹配到视图组件都会被缓存
vuex
state
单一状态树
getters
基本使用:
相当于computed计算属性
参数和传入对象
pow(state){ return state.counter * state.counter }, more20stu(state){ return state.students.filter(s => s.age > 20) }, more20stuLength(state, getters){ return getters.more20stu.length }, moreAge(state){ // return function (age){ // return state.students.filter(s => s.age > age) // } return age => { return state.students.filter(s => s.age > age) } } mutation
主要包括两部分:
字符串的事件类型(type);
一个回调函数(hander),该回调函数的第一个参数就是state
在通过mutation更新数据的时候,希望携带的额外的参数被称为mutation的载荷(PayLoad)
提交风格
this.$store.commit({ type: 'change', count: 20 }) change(state,payload){ state.count = payload.count } 响应规则
- 提前在store中初始化好所需的属性
- 当给store中的对象添加新属性时,使用下面的方式:
- 使用Vue.set(obj, 'new Prop' , 123) ,可以添加到响应式系统中
- 用新对象给就对象赋值
- 当给store中的对象删除属性时,使用
Vue.delete(obj, 'prop')
常量类型
mutation-types.js
同步函数
action:用来代替mutation进行异步操作
actions:{ aUpdateInfo(context, payload) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { context.commit('updateInfo'); console.log(payload); resolve('1111111') }, 1000) }) } }, update(){ this.$store .dispatch('aUpdateInfo', '我是携带的信息') .then(res => { console.log('里面完成了提交'); console.log(res); }) } module
vue使用单一状态树,就意味着很多状态都会交给vuex管理,当应用变得复杂的时候,store就变得相当臃肿,所以vuex允许将store分割成模块(module),而每个模块都可以拥有自己的state,mutations,actions等
网络封装(axios)
特点
在浏览器发送HMLHttpRequest请求
在node.js中发送http
支持Promise API
拦截请求和响应
转换请求和响应
使用
多种请求方式
- axios(config)
- axios.request(config)
- axios.get(url[,config])
- axios.delete(url,[config])
- axios.head(url,[config])
- axios.post(url,[,data[,config]])
- axios.put(url,[,data[,config]])
- axios.patch(url,[,data[,config]])
发送并发请求
- 使用axios.all,可以放入多个请求的数组
- axios.all[]返回的结果是一个数组,使用axios.spread可将数组[res1,res2]展开为res1,res2
全局配置
- 请求地址 : url:'/user
- 请求类型 : methods: 'get'
- 请求根路径 : baseURL:'http://www.mt.com/api'
- 请求前的数据处理 : transformRequest: [function(data){}],
- 请求后的数据处理 : transformRequest:[function(data){}]
- 自定义的请求头 : header:{'X-Request-With':'XMLHttprequest'},
- URL查询对象 : params:{id:12}
- 查询对象序列化函数
- request body(请求体)
- 超时设置
- 跨域是否带Token
- 自定义请求处理
- 身份验证信息
- 相应的数据格式
axios实例
const instance1 = axios.create({ baseURL: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000', timeout: 5000 }) instance1({ url: '/home/multidata' }).then(res => { console.log(res); }) 



