- A+
这里给大家分享我在网上总结出来的一些知识,希望对大家有所帮助
原型和原型链
1. 原型
每个JS对象一定对应一个原型对象,并从原型对象继承属性和方法
1.1 __proto__
对象的__proto__属性值就是对象的原型对象
此属性是过时的语法,现在建议使用Object.getPrototypeof(obj)
函数也是对象,因此也有__proto__属性
1.2 Prototype
函数的prototype属性值就是函数的原型对象
定义:给其他对象提供共享属性的对象,prototype 本身也是对象,只是被用以承担某个职能
当说 prototype 对象时,实际上说的是 “xxx 函数对象的 prototype 对象”
1.3 constructor
每个原型都有一个 constructor 属性指向关联的构造函数
实例访问 constructor 属性是获取的原型对象的构造函数
function Person(age) { this.age = age; } let p = new Person(50); console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person); // true console.log(p.constructor === Person); // true 会查找原型对象
对于引用类型来说 constructor 属性值是可以修改的,但是对于基本类型来说是只读的,因为创建他们的是只读的原生构造函数(native constructors)
2. 原型链
每个对象拥有一个原型对象,通过 __proto__ 指针指向上一个原型 ,并从中继承方法和属性,同时原型对象也可能拥有原型,这样一层一层,最终指向 null。这种关系被称为原型链 (prototype chain),通过原型链一个对象会拥有定义在其他对象中的属性和方法。
因此,当读取实例的属性时,如果找不到,就会查找与对象关联的原型中的属性,如果还查不到,就去找原型的原型,一直找到最顶层为止。
2.1 原型链知识点
-
原型链的尽头(root)是
Object.prototype。所有对象(除null)均从Object.prototype继承属性 -
Object.prototype.__proto__值是null,原型链终止 -
Function.prototype和Function.__proto__为同一对象意味着:
Object/Array/String等等构造函数本质上和Function一样,均继承于Function.prototype -
Function.prototype直接继承root(Object.prototype) -
继承的原型链:
Object.prototype(root)<---Function.prototype<---Function|Object|Array... -
对象的
__proto__指向自己构造函数的prototype -
ES规范定义对象字面量({})的原型就是
Object.prototype
2.2 Object和Function的鸡和蛋的问题
Function.prototype是个不同于一般函数(对象)的函数(对象)Function.prototype像普通函数一样可以调用,但总是返回undefined。- 普通函数实际上是
Function的实例,即普通函数继承于Function.prototype。func.__proto__ === Function.prototype。 Function.prototype继承于Object.prototype,并且没有prototype这个属性。func.prototype是普通对象,Function.prototype.prototype是null。- 总结,
Function.prototype其实是个另类的函数,可以独立于/先于Function产生。
- Object本身是个(构造)函数,是Function的实例,即
Object.__proto__就是Function.prototype
问题总结:
先有Object.prototype(原型链顶端),Function.prototype继承Object.prototype而产生,最后,Function和Object和其它构造函数继承Function.prototype而产生
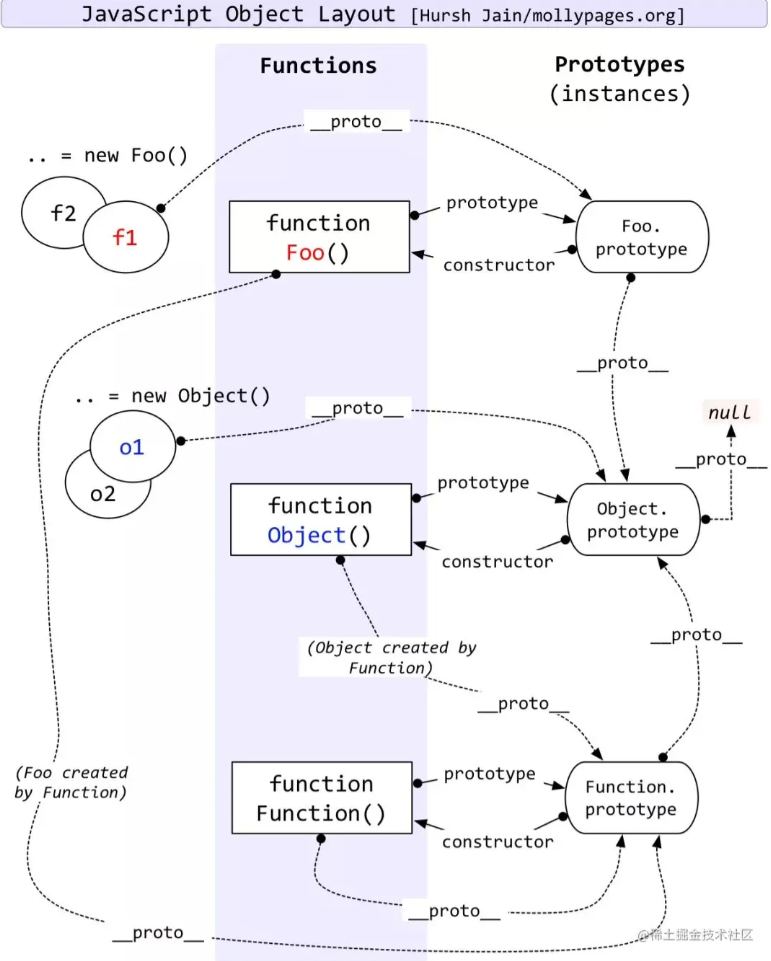
2.3 原型链图解
原型和原型链经典关系图
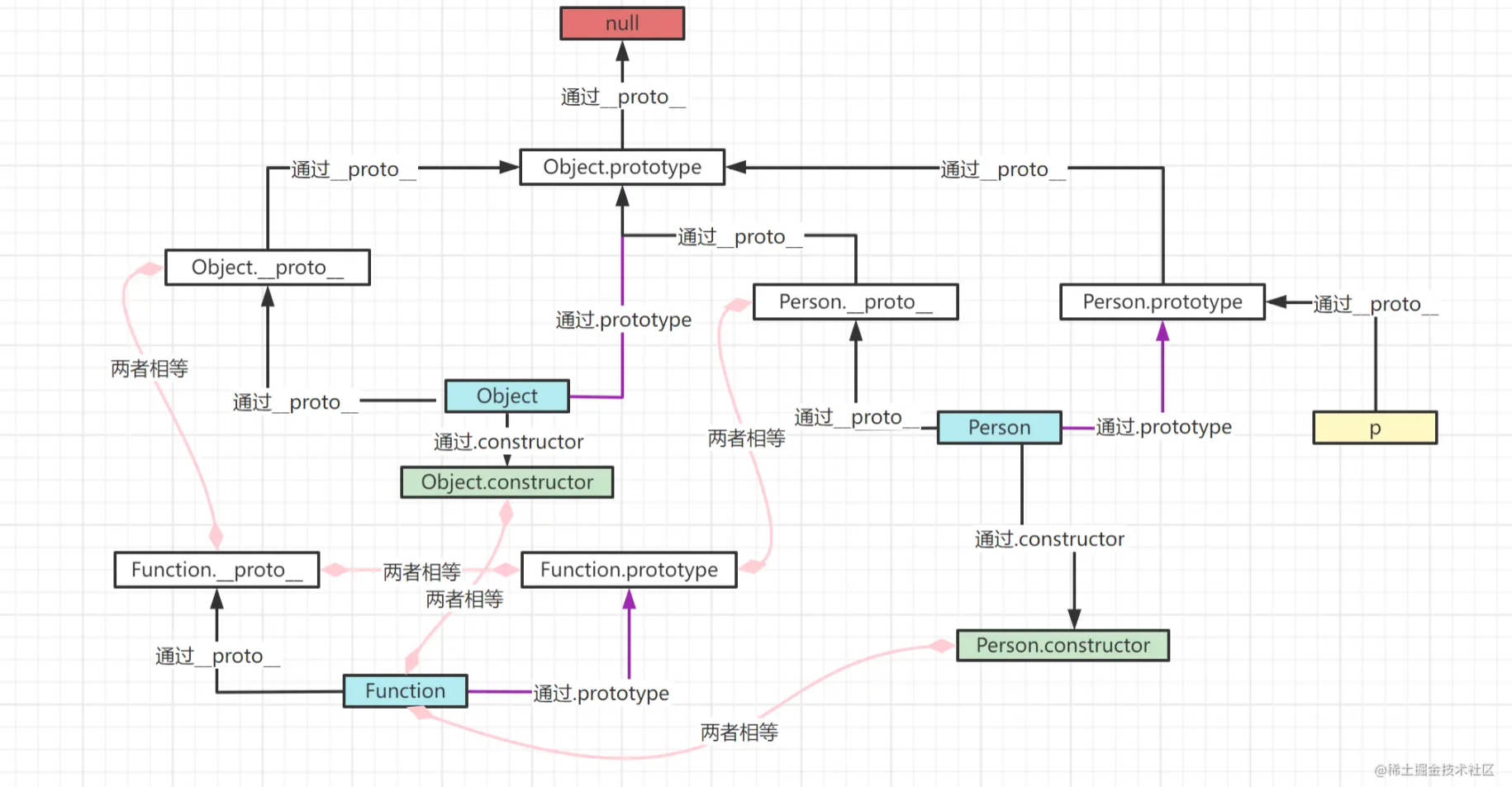
自己画的原型图
图解描述:
Person、Object、Function是函数对象,具备prototype属性,其他对象是只有__proro__
获取原型对象
Person.__proto__及Object.__proto__与Function.__proto__相等,是ƒ () { [native code] }
Person.__proto__及Object.__proto__与Function.__proto__的原型对象为Object.prototype
Function.__proto__和Function.prototype值相等,为空函数: ƒ () { [native code] }
Person.constructor、Object.constructor与Function值相等,为: ƒ Function() { [native code] }
原型链代码输出结果
function Person(name) { this.name = name } var p2 = new Person('king'); console.log(p2.__proto__) //Person.prototype console.log(p2.__proto__.__proto__) //Object.prototype console.log(p2.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__) // null console.log(p2.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__) //null后面没有了,报错 console.log(p2.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__) //null后面没有了,报错 console.log(p2.constructor)//Person console.log(p2.prototype)//undefined p2是实例,没有prototype属性 console.log(Person.constructor)//Function 一个空函数 console.log(Person.prototype) //打印出Person.prototype这个对象里所有的方法和属性 console.log(Person.prototype.constructor)//Person console.log(Person.prototype.__proto__)// Object.prototype console.log(Person.__proto__) //Function.prototype console.log(Function.prototype.__proto__)//Object.prototype console.log(Function.__proto__)//Function.prototype console.log(Object.__proto__)//Function.prototype console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__)//null console.log(Function); // ƒ Function() { [native code] } 空函数,名为Function console.log(Object.constructor); // ƒ Function() { [native code] } console.log(Person.constructor); // ƒ Function() { [native code] } console.log(Function === Object.constructor); // true console.log(Function === Person.constructor); // true console.log(Function.__proto__); // ƒ () { [native code] } console.log(Function.prototype); // ƒ () { [native code] } console.log(Function.__proto__ == Function.prototype); // true console.log(Function.__proto__.__proto__ === Object.prototype) // true console.log(Function.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype) // true