- A+
现在VUE3已经有一段时间了,也慢慢普及起来了。不过因为一直还在使用VUE2的原因还是去了解和学了下它的源码,毕竟VUE2也不会突然就没了是吧,且VUE3中很多原理之类的也是类似的。然后就准备把VUE3搞起来了是吧。VUE2源码使用的是roullup进行打包的,还使用了Flow进行静态类型检测(该库使用的已经不多了,且VUE3已经使用TypeScript进行开发了,有类型检测了)。若是没怎么接触过Vue2,直接Vue3会更划算些,结构之类的也更清晰了。
篇幅有限只探讨了核心的一些过程。
VUE2项目结构与入口
主要目录结构:
vue2源码仓库:https://github.com/vuejs/vue
clone后可以看到大概如下结构:
|----benchmarks 性能测试
|----scripts 脚本文件
|----scr 源码
| |----compiler 模板编译相关
| |----core vue2核心代码
| |----platforms 平台相关
| |----server 服务端渲染
| |----sfc 解析单文件组件
| |----shared 模块间共享属性和方法
package.json入口:
// package.json 中指定了roullup的配置文件及打包参数 "scripts": { "dev": "rollup -w -c scripts/config.js --environment TARGET:web-full-dev", "dev:cjs": "rollup -w -c scripts/config.js --environment TARGET:web-runtime-cjs-dev", "dev:esm": "rollup -w -c scripts/config.js --environment TARGET:web-runtime-esm", } // 在/scripts/config.js 可以看到在接受到参数后 打包入口最终在 /src/platforms下文件中 构建参数与版本的说明
可以看到rollup打包或者调试的时候后面更了很多参数,不同参数就能生成不同内容的版本,参数说明如下:
- web-runtime: 运行时,无法解析传入的template
- web-full:运行时 + 模板编译
- web-compiler:仅模板编译
- web-runtime-cjs web-full-cjs:cjsCommonJS打包
- web-runtime-esm web-full-esm :esm 语法(支持import export)
- web-full-esm-browser:浏览器中使用
- web-server-renderer:服务端渲染
注:在使用CLI脚手架开发时,一般都是选择web-runtime是因为,脚手架中有vue-loader会将模板转为render函数了,所以不需要再模板编译了。
入口深入与源码的构建,调试
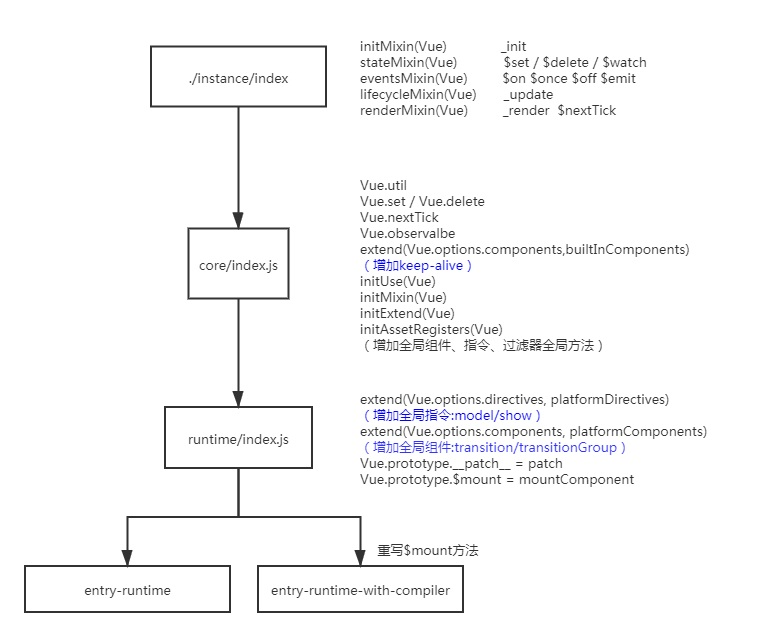
我们可以在/platforms目录下找到,最外层的入口。但这个入口有经过层层包装,添加了些方法后,最后才会到创建VUE实例的入口。以entry-runtime-with-compiler.js为例,
entry-runtime-with-compiler 重写了$mount,主要增加了对模板的处理方法。:
- 没有
template则尝试从el中取dom作template - 有
template则直接使用传入的template - 没则将
template转化为render函数,放在$options上
它的Vue又是从./runtime/index导进来的。runtime/index.js有公共的$mount方法,还增加了:
- directives (全局指令:model,show)
- components (全局组件:transition,transitionGroup)
- patch(浏览器环境)
详细流程如下图:
开启调试:
在package.json项中增加sourcemap配置,如:
"scripts": { "dev": "rollup -w -c scripts/config.js --sourcemap --environment TARGET:web-full-dev", ....... } 然后npm run dev就可以在源码中debugger进行调试了。
VUE基本代码的执行在源码中的核心流程
比如在页面中有如下代码,它主要涉及到Vue中的技术有:模板语法,数据双向绑定,计算属性,侦听器。
点击查看主要代码
<div id="app"> <p>{{fullName}}:{{fullName}}-{{formBY}}</p> </div> const vm = new Vue({ el: "#app", data() { return { firstName: "Shiina", lastName: "Mashiro", formBY: "flytree-cnblogs", arr: [1, 2, 3, ["a"]], }; }, computed: { fullName() { return this.firstName + this.lastName; } }, watch: { firstName(newValue, oldValue) { console.log(newValue, oldValue) } } }); setTimeout(() => { vm.firstName = 'flytree' }, 1000); 我们可以把核心(细节后面再展开,先有个整体把握)的执行流程梳理下如下图:
创建响应式数据
要实现数据的双向绑定,就要创建响应式数据,原理就是重写了data中每项数据的getter和setter,这样就可以拦截到每次的取值或者改值的操作了,取值的时候收集依赖,改值的时候通知notify:
点击查看代码
// 路径 /scr/core/observer/index.js export function defineReactive() { const dep = new Dep() const property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key) if (property && property.configurable === false) { return } // cater for pre-defined getter/setters const getter = property && property.get const setter = property && property.set if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) { val = obj[key] } let childOb = !shallow && observe(val) Object.defineProperty(obj, key, { enumerable: true, configurable: true, get: function reactiveGetter() { const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val if (Dep.target) { dep.depend() if (childOb) { childOb.dep.depend() if (Array.isArray(value)) { dependArray(value) } } } return value }, set: function reactiveSetter(newVal) { const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val /* eslint-disable no-self-compare */ if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) { return } /* eslint-enable no-self-compare */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) { customSetter() } // #7981: for accessor properties without setter if (getter && !setter) return if (setter) { setter.call(obj, newVal) } else { val = newVal } childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal) dep.notify() } }) } 模板编译
compileToFunctions进行模板编译,主要流程就是:
- 使用正则解析模板,然后将其转化卫AST抽象语法树。
- 然后根据AST抽象语法树拼装
render函数。
比如上面的代码
template: "<div id="app">n <p>{{fullName}}:{{fullName}}-{{formBY}}</p>n 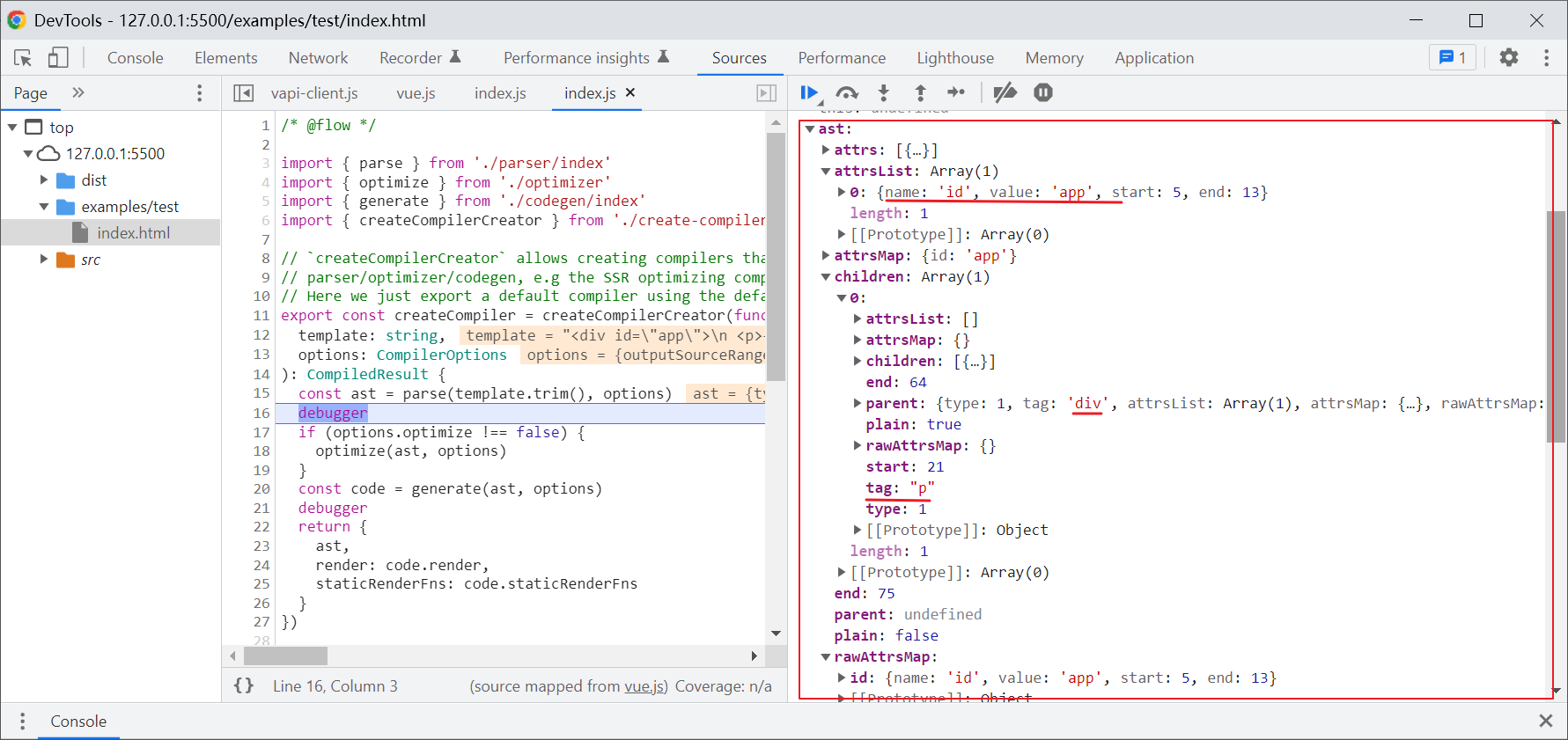
生成的render函数:
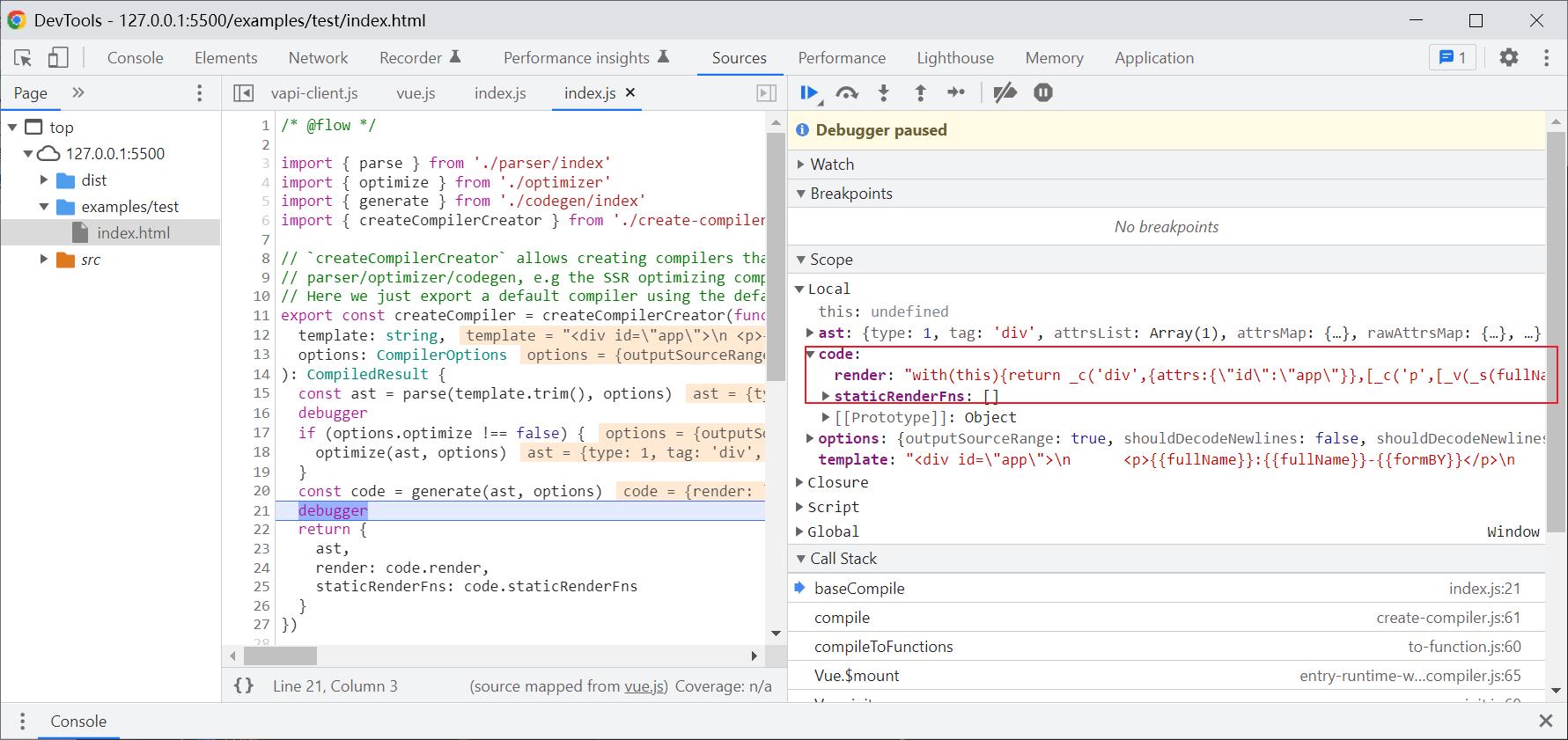
"with(this){ return _c('div',{attrs:{"id ":"app "}}, [_c('p',[_v(_s(fullName)+": "+_s(fullName)+" - "+_s(formBY))])]) }" 使用with,vue实列执行到这个方法时,则会去找当前实例的属性。
而_c,_s,_v等函数是用来将对应类型节点转换位虚拟dom的,render执行后就能生成对应的虚拟dom树了。
依赖收集
在看依赖收集前,可以想下以下问题:
| 问 | 答 |
|---|---|
| 什么时候进行依赖收集? | data中项被取值(其getter执行) |
| 什么时候执行getter? | _render函数执行 |
| 什么时候执行_render? | _update函数执行 |
| 什么时候执行_update? | data项中getter执行 |
| 什么时候执行data项中get方法? | 模板中取值 |
这时我们再看下get的来源和去处,看下具体的流程:
可以看到:
1.取值:在模板中取值的时候它就会进行依赖收集,执行dep.depend(), 最后会去重的watcher存在依赖的subs[]中。去重是,如果模板中重复取了两次值,那也不会重复收集watcher。
2.改值:在值发生变更的时候,就会触发dep.notify(),会遍历执行其dep.subs中的所有watcher.update(),最后还是会执行到watcher.get(),那么就执行了_update(_render())把变化更新到dom上了。
Dep类源码:
点击查看代码
export default class Dep { constructor () { this.id = uid++ this.subs = [] } addSub (sub) { this.subs.push(sub) } removeSub (sub) { remove(this.subs, sub) } depend () { if (Dep.target) { Dep.target.addDep(this) } } notify () { // stabilize the subscriber list first const subs = this.subs.slice() if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !config.async) { // subs aren't sorted in scheduler if not running async // we need to sort them now to make sure they fire in correct // order subs.sort((a, b) => a.id - b.id) } for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) { subs[i].update() } } } Watcher类源码:
点击查看主要代码
export default class Watcher { constructor(vm, expOrFn, cb, options, isRenderWatcher) { this.vm = vm if (isRenderWatcher) { vm._watcher = this } vm._watchers.push(this) // options if (options) { this.deep = !!options.deep this.user = !!options.user this.lazy = !!options.lazy this.sync = !!options.sync this.before = options.before } else { this.deep = this.user = this.lazy = this.sync = false } this.cb = cb this.id = ++uid // uid for batching this.active = true this.dirty = this.lazy // for lazy watchers this.deps = [] this.newDeps = [] this.depIds = new Set() this.newDepIds = new Set() this.expression = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' ? expOrFn.toString() : '' // parse expression for getter if (typeof expOrFn === 'function') { // 渲染watcher时就gettr就传入了 _update(_render()) this.getter = expOrFn } else { this.getter = parsePath(expOrFn) if (!this.getter) { this.getter = noop process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn( `Failed watching path: "${expOrFn}" ` + 'Watcher only accepts simple dot-delimited paths. ' + 'For full control, use a function instead.', vm ) } } // 在计算属性创建watcher的时候lazy为true this.value = this.lazy ? undefined : this.get() } /** * Evaluate the getter, and re-collect dependencies. */ get() { pushTarget(this) let value const vm = this.vm try { value = this.getter.call(vm, vm) } catch (e) { if (this.user) { handleError(e, vm, `getter for watcher "${this.expression}"`) } else { throw e } } finally { // "touch" every property so they are all tracked as // dependencies for deep watching if (this.deep) { traverse(value) } popTarget() this.cleanupDeps() } return value } /** * Add a dependency to this directive. */ addDep(dep) { const id = dep.id if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) { this.newDepIds.add(id) this.newDeps.push(dep) if (!this.depIds.has(id)) { dep.addSub(this) } } } /** * Clean up for dependency collection. */ cleanupDeps() { let i = this.deps.length while (i--) { const dep = this.deps[i] if (!this.newDepIds.has(dep.id)) { dep.removeSub(this) } } let tmp = this.depIds this.depIds = this.newDepIds this.newDepIds = tmp this.newDepIds.clear() tmp = this.deps this.deps = this.newDeps this.newDeps = tmp this.newDeps.length = 0 } /** * Subscriber interface. * Will be called when a dependency changes. */ update() { /* istanbul ignore else */ if (this.lazy) { this.dirty = true } else if (this.sync) { this.run() } else { queueWatcher(this) } } /** * Scheduler job interface. * Will be called by the scheduler. */ run() { if (this.active) { const value = this.get() if ( value !== this.value || // Deep watchers and watchers on Object/Arrays should fire even // when the value is the same, because the value may // have mutated. isObject(value) || this.deep ) { // set new value const oldValue = this.value this.value = value if (this.user) { const info = `callback for watcher "${this.expression}"` invokeWithErrorHandling(this.cb, this.vm, [value, oldValue], this.vm, info) } else { this.cb.call(this.vm, value, oldValue) } } } } /** * Evaluate the value of the watcher. * This only gets called for lazy watchers. */ evaluate() { this.value = this.get() this.dirty = false } /** * Depend on all deps collected by this watcher. */ depend() { let i = this.deps.length while (i--) { this.deps[i].depend() } } /** * Remove self from all dependencies' subscriber list. */ teardown() { if (this.active) { // remove self from vm's watcher list // this is a somewhat expensive operation so we skip it // if the vm is being destroyed. if (!this.vm._isBeingDestroyed) { remove(this.vm._watchers, this) } let i = this.deps.length while (i--) { this.deps[i].removeSub(this) } this.active = false } } } 更新到dom树的细节
从上面步骤分析下来,一般情况下,watcher实例的中的get()执行了,就能触发,dom更新了。就是走了updateComponent
// 此方法在 core/instance/lifecycle.js updateComponent = () => { vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating) } _render执行后会生成虚拟dom,而_update就会执行patch(__patch__)更新对比后更新dom了。
_update源码:
点击查看代码
export function lifecycleMixin (Vue) { Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode, hydrating) { const vm = this const prevEl = vm.$el const prevVnode = vm._vnode const restoreActiveInstance = setActiveInstance(vm) vm._vnode = vnode // Vue.prototype.__patch__ is injected in entry points // based on the rendering backend used. if (!prevVnode) { // initial render vm.$el = vm.__patch__(vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false /* removeOnly */) } else { // updates vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode) } restoreActiveInstance() // update __vue__ reference if (prevEl) { prevEl.__vue__ = null } if (vm.$el) { vm.$el.__vue__ = vm } // if parent is an HOC, update its $el as well if (vm.$vnode && vm.$parent && vm.$vnode === vm.$parent._vnode) { vm.$parent.$el = vm.$el } // updated hook is called by the scheduler to ensure that children are // updated in a parent's updated hook. } } patch进行diff优化
patch导出:
// platforms/web/runtime/patch.js export const patch: Function = createPatchFunction({ nodeOps, modules }) 最后createPatchFunction的源码在core/vdom/patch.js
Diff大概的流程:
判断是否是相同节点:sameVnode判断标签和key是否相同。
diff算法是用来比较两个虚拟dom的更新情况的,而且是同级比较的。
在diff算法中有四个指针,
在新的虚拟dom中的两个指针,新前(在前面的指针),新后(在后面的指针)。
在旧的虚拟dom中的两个指针,旧前(在前面的指针),旧后(在后面的指针)。
前指针的特点:
- 初始位置在最前面,也就是说children数组中的第0位。
- 前指针只能向后移动。
后指针的特点:
- 初始位置在最后面,也就是说在children数组中的第length-1位。
- 后指针只能向前移动。
每次比较可能进行以下四种比较:
- 新前和旧前。匹配则,前指针后移一位,后指针前移一位。
- 新后和旧后。匹配则,前指针后移一位,后指针前移一位。
- 新后和旧前。匹配则,将所匹配的节点的dom移动到旧后之后,虚拟dom中将其设位undefined,指针移动。
- 新前和旧后。匹配则,将所匹配的节点的dom移动到旧前之前,虚拟dom中将其设位undefined,指针移动。
匹配的步骤是按此顺序从一到四进行匹配,但若之中有匹配成功的则不进行之后的匹配,比如第2种情况匹配,则不会进行3,4的匹配了。
上面四种匹配是对push, shift, pop, unshift ,reveres ,sort 操作进行优化,但若以上的四种情况都未曾匹配到,则会以新虚拟dom中为匹配的这项当作查找的目标,在旧虚拟dom中进行遍历查找:
- 若查找到,则将dom中找到这项移动旧前之前,其虚拟dom中位置则设为undefined。然后新前指针移动一位。
- 若未找到,则将新前所指的这项(也是查找的目标项),生成dom节点,插入到旧前之前上,而后新前指针移动一位。




