- A+
最近在公司的项目中,编写了几个自定义的 Exception 类。提交 PR 的时候,sonarqube 提示这几个自定义异常不符合 ISerializable patten. 花了点时间稍微研究了一下,把这个问题解了。今天在此记录一下,可能大家都会帮助到大家。
自定义异常
编写一个自定义的异常,继承自 Exception,其中定义一个 ErrorCode 来存储异常编号。平平无奇的一个类,太常见了。大家觉得有没有什么问题?
[Serializable] public class MyException : Exception { public string ErrorCode { get;} public MyException(string message, string errorCode) : base(message) { ErrorCode = errorCode; } } 如我们对这个异常编写一个简单的单元测试。步骤如下:
[TestMethod()] public void MyExceptionTest() { // arrange var orignalException = new MyException("Hi", "1000"); var bf = new BinaryFormatter(); var ms = new MemoryStream(); // act bf.Serialize(ms, orignalException); ms.Seek(0, 0); var newException = bf.Deserialize(ms) as MyException; // assert Assert.AreEqual(orignalException.Message, newException.Message); Assert.AreEqual(orignalException.ErrorCode, newException.ErrorCode); } 这个测试主要是对一个 MyException 的实例使用 BinaryFormatter 进行序列化,然后反序列化成一个新的对象。将新旧两个对象的 ErrorCode 跟 Message 字段进行断言,也很简单。
让我们运行一下这个测试,很可惜失败了。测试用例直接抛了一个异常,大概是说找不到序列化构造器。
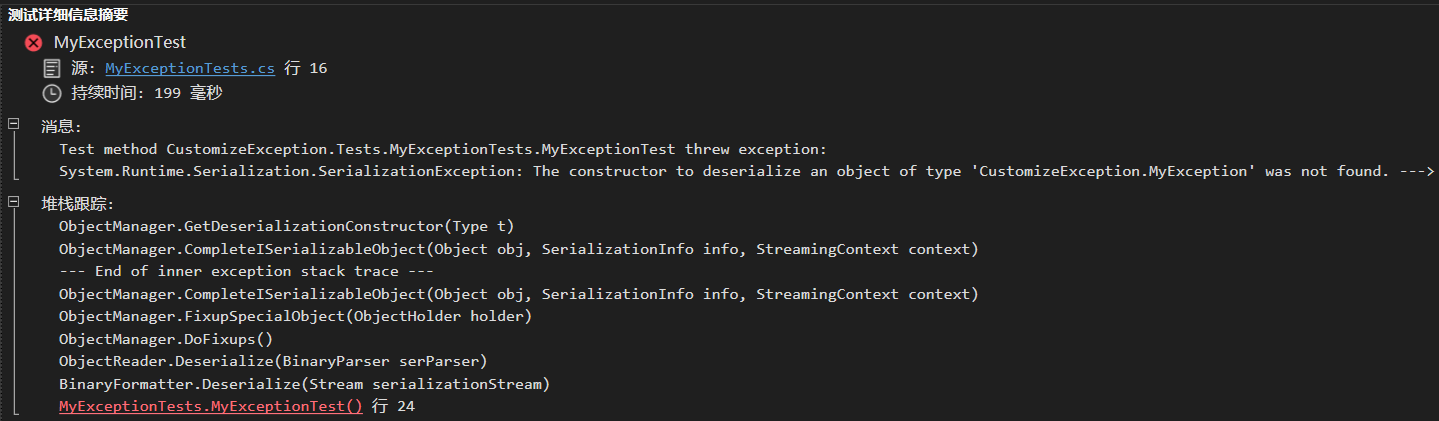
Designing Custom Exceptions Guideline
简单的搜索了一下,发现微软有对于自定义 Exception 的
Designing Custom Exceptions
。
总结一下大概有以下几点:
-
一定要从 System.Exception 或其他常见基本异常之一派生异常。
-
异常类名称一定要以后缀 Exception 结尾。
-
应使异常可序列化。 异常必须可序列化才能跨越应用程序域和远程处理边界正确工作。
-
一定要在所有异常上都提供(至少是这样)下列常见构造函数。 确保参数的名称和类型与在下面的代码示例中使用的那些相同。
public class NewException : BaseException, ISerializable { public NewException() { // Add implementation. } public NewException(string message) { // Add implementation. } public NewException(string message, Exception inner) { // Add implementation. } // This constructor is needed for serialization. protected NewException(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context) { // Add implementation. } } 按照上面的 guideline 重新改一下我们的 MyException,主要是添加了几个构造器。修改后的代码如下:
[Serializable] public class MyException : Exception { public string ErrorCode { get; } public MyException() { } public MyException(string message, string errorCode) : base(message) { ErrorCode = errorCode; } public MyException(string message, Exception inner): base(message, inner) { } protected MyException(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context) { } } 很可惜按照微软的 guideline 单元测试还是没通过。获取 Message 字段的时候会直接 throw 一个 Exception。
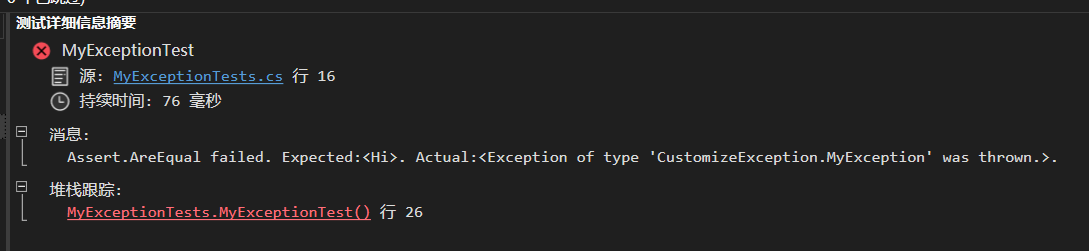
那么到底该怎么实现呢?
正确的方式
我们还是按照微软 guideline 进行编写,但是在序列化构造器的上调用 base 的构造器。并且 override 基类的 GetObjectData 方法。
[Serializable] public class MyException : Exception { public string ErrorCode { get; } public MyException() { } public MyException(string message, string errorCode) : base(message) { ErrorCode = errorCode; } public MyException(string message, Exception inner): base(message, inner) { } protected MyException(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context): base(info, context) { // Set the ErrorCode value from info dictionary. ErrorCode = info.GetString("ErrorCode"); } public override void GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context) { if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(ErrorCode)) { // Add the ErrorCode to the SerializationInfo dictionary. info.AddValue("ErrorCode", ErrorCode); } base.GetObjectData(info, context); } } 在序列化构造器里从 SerializationInfo 对象里恢复 ErrorCode 的值。调用 base 的构造可以确保基类的 Message 字段被正确的还原。这里与其说是序列化构造器不如说是反序列化构造器,因为这个构造器会在反序列化恢复成对象的时候被调用。
protected MyException(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context): base(info, context) { // Set the ErrorCode value from info dictionary. ErrorCode = info.GetString("ErrorCode"); } 这个 GetObjectData 方法是 ISerializable 接口提供的方法,所以基类里肯定有实现。我们的子类需要 override 它。把自己需要序列化的字段添加到 SerializationInfo 对象中,这样在上面反序列化的时候确保可以把字段的值给恢复回来。记住不要忘记调用 base.GetObjectData(info, context), 确保基类的字段数据能正确的被序列化。
public override void GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context) { if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(ErrorCode)) { // Add the ErrorCode to the SerializationInfo dictionary. info.AddValue("ErrorCode", ErrorCode); } base.GetObjectData(info, context); } 再次运行单元测试,这次顺利的通过了?,说明 Message 跟 ErrorCode 字段在反序列化后成功的被恢复了。
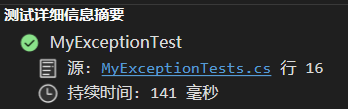
总结
自定义异常是大家日常编码过程中非常常见的操作。但是看来要写好一个自定义异常类也不是那么简单。总结一下需要注意以下几点:
- 添加 [Serializable] Attribute
- 遵守微软的 guideline,特别是构造器部分 Designing Custom Exceptions Guideline
- 在序列化构造器对字段值进行恢复,不要忘记调用基类的序列化构造器
- 重写
GetObjectData方法,把需要序列化的字段添加到SerializationInfo对象上,同样不要忘记调用基类的GetObjectData
这个问题虽然在自定义 Exception 上暴露出来,其实可以推广到所有实现ISerializable接口的类都需要注意 3,4 两点。
关注我的公众号一起玩转技术





