- A+
1. 为什么选择使用泛型集合
存在的问题
ArrayList arrylist = new ArrayList() { 14, "hello", 29.7, true}; arrylist.Add("world");// object double dsum = 0; foreach(var item in arrylist) { dsum += Convert.ToDouble(item); // 出现异常 }
1、存取数据需要进行装箱拆箱 2、数据类型转换存在隐患
性能对比
非泛型集合性能
[Test] public void Test1() { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); ArrayList arrayList = new(); for (int i = 0; i < 2000000; i++) { arrayList.Add(i); // 装箱 } long sum = 0; foreach (var item in arrayList) { sum += Convert.ToInt64(item); } watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("非泛型集合耗时(ms):"+watch.ElapsedMilliseconds); }
输出结果:非泛型集合耗时(ms):258
泛型集合性能
[Test] public void Test1() { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); var arrayList = new List<int>(); for (int i = 0; i < 2000000; i++) { arrayList.Add(i); } long sum = 0; foreach (var item in arrayList) { sum += Convert.ToInt64(item); } watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("泛型集合耗时(ms):"+watch.ElapsedMilliseconds); }
输出结果:泛型集合耗时(ms):25
2. List<T> 集合
使用场景:
-
在Linq 中比较常见
-
存储数据
声明
声明泛型集合
List<T> 集合名=new List<T>()
例如:
//值类型 List<int> list = new List<int>(); //引用类型 List<PersonModel> personList = new List<PersonModel>()
1、T只是占位符,会被传递的数据类型替换。 2、实例化List时传入相对应的数据类型 3、长度以2倍速度扩容
List<T> 常用属性
| Count | List集合中当前存储的元素个数 |
|---|---|
| Capacity | List集合当前容量 Capacity>=Count |
List<int> list = new List<int>() { 2, 3, 7, 5, 9 }; // 集合初始化器 Count : 5 Capacity : 8
List<T> 常用方法
| Add() | 添加到List集合尾部 Add(元素) 如:strlist.Add(“me”) |
|---|---|
| Insert() | 添加到List集合指定位置 Insert(下标,元素) 如:strlist.Insert(2,”Hi”) |
| Remove() | 删除List集合中的元素 Remove(元素) 如:strlist.Remove(“c”) |
| RemoveAt() | 删除List集合中指定下标的元素 RemoveAt(下标)如:strlist.RemoveAt(3) |
| RemoveRange() | 删除List集合中指定范围的元素 RemoveRange(下标,个数), 如:strlist.RemoveRange(1,2) |
| Clear() | 清空List集合中所有元素 Clear() |
| First() | 返回List集合中第一个元素 |
| FirstOrDefault () | 返回List集合中第一个元素为空是返回默认值 |
| Last() | 返回List集合中最后一个元素 |
| LastOrDefault () | 返回List集合最后一个元素为空时返回默认值 |
List<int> list = new List<int>() { 2, 3, 7, 5, 9 }; list.Add(10); // 2, 3, 7, 5, 9,10 list.Insert(2,6); // 2, 3,6, 7, 5, 9,10 list.Remove(2); // 3,6, 7, 5, 9,10 list.RemoveAt(0); // 6, 7, 5, 9,10 list.RemoveRange(1,2); // 6,9,10 list.First();// 6 list.FirstOrDefault(); // 6 list.Last();// 10 list.LastOrDefault(); // 10 list.Clear(); // 集合为空
3. Stack<T> 栈
特点:先进后出,后进先出
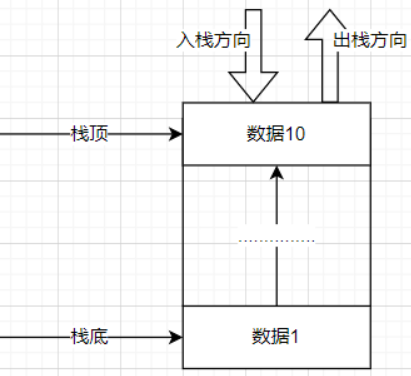
[Test] public void Test1() { Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>(); stack.Push(10); // 压栈 10 stack.Push(9); // 9,10 stack.Push(8); // 8,9,10 var peek = stack.Peek(); // 8 返回最顶的元素 var item = stack.Pop();// 8 , 移除并返回最顶的元素,stack 还剩下 9,10 foreach (var s in stack) { Console.WriteLine(s); // 输出 9 ,10 } }
4. Queue<T> 队列
特点:先进先出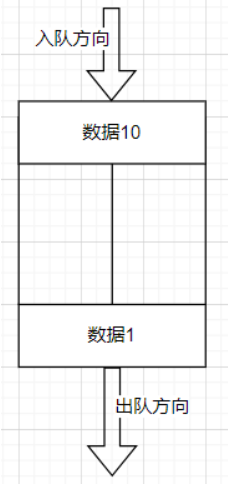
[Test] public void Test1() { Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>(); queue.Enqueue(10); // 入队 queue.Enqueue(9); queue.Enqueue(8); queue.Enqueue(7); Console.WriteLine(queue.Peek()); // 返回最开始的元素,10(出队方向的第一个元素) var item = queue.Dequeue();// 删除出队方向的第一个元素 并返回它的值 ,10 foreach (var q in queue) { Console.WriteLine(q); // 9,8,7 } }
5. SortedList<TKey,TValue> 类
-
程序集: System.Collections.dll
表示基于相关的 IComparer 实现按键进行排序的键/值对的集合。
-
TKey 集合中的键的类型。
-
TValue 集合中值的类型。
快速入门
[Test] public void Test1() { // 成绩列表 SortedList<string,int> scoreList = new SortedList<string,int>(); scoreList["b"] = 80; scoreList["c"] = 50; scoreList.Add("a",100); foreach (var score in scoreList) { Console.WriteLine($"科目:{score.Key},成绩:{score.Value}"); } }
输出结果:
科目:a,成绩:100
科目:b,成绩:80
科目:c,成绩:50
详细案例
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Example { public static void Main() { // 创建一个键值对都是string 类型的集合 SortedList<string, string> openWith = new SortedList<string, string>(); // 初始化一些没有重复键的元素,但对应的值,有些元素是重复的 openWith.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); openWith.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("dib", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); // 如果添加一个已经存在的键值对,则会抛出异常 try { openWith.Add("txt", "winword.exe"); } catch (ArgumentException) { Console.WriteLine("An element with Key = "txt" already exists."); } // 元素的键可作为集合的索引来访问元素 Console.WriteLine("For key = "rtf", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // 通过键索引,可修改其所关联的值 openWith["rtf"] = "winword.exe"; Console.WriteLine("For key = "rtf", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // 如果键不存在,则会新增一个键值对数据 openWith["doc"] = "winword.exe"; // 如果请求的键不存在,则会抛出异常 try { Console.WriteLine("For key = "tif", value = {0}.", openWith["tif"]); } catch (KeyNotFoundException) { Console.WriteLine("Key = "tif" is not found."); } // 当一个程序经常要尝试的键,结果却不是 在列表中,TryGetValue可以是一个更有效的 // 获取值的方法。 string value = ""; if (openWith.TryGetValue("tif", out value)) { Console.WriteLine("For key = "tif", value = {0}.", value); } else { Console.WriteLine("Key = "tif" is not found."); } // 判断是否包含键 if (!openWith.ContainsKey("ht")) { openWith.Add("ht", "hypertrm.exe"); Console.WriteLine("Value added for key = "ht": {0}", openWith["ht"]); } // 遍历循环,元素被检索为KeyValuePair对象 Console.WriteLine(); foreach( KeyValuePair<string, string> kvp in openWith ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}, Value = {1}", kvp.Key, kvp.Value); } // 获取集合中的Values 列表 IList<string> ilistValues = openWith.Values; // 打印出所有的值列表 Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in ilistValues ) { Console.WriteLine("Value = {0}", s); } // 通过索引获取值 Console.WriteLine("nIndexed retrieval using the Values " + "property: Values[2] = {0}", openWith.Values[2]); // 获取所有的Key IList<string> ilistKeys = openWith.Keys; // 打印出所有的键列表 Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in ilistKeys ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}", s); } // 通过索引获取Key Console.WriteLine("nIndexed retrieval using the Keys " + "property: Keys[2] = {0}", openWith.Keys[2]); // 移除元素 Console.WriteLine("nRemove("doc")"); openWith.Remove("doc"); if (!openWith.ContainsKey("doc")) { Console.WriteLine("Key "doc" is not found."); } } } /* This code example produces the following output: An element with Key = "txt" already exists. For key = "rtf", value = wordpad.exe. For key = "rtf", value = winword.exe. Key = "tif" is not found. Key = "tif" is not found. Value added for key = "ht": hypertrm.exe Key = bmp, Value = paint.exe Key = dib, Value = paint.exe Key = doc, Value = winword.exe Key = ht, Value = hypertrm.exe Key = rtf, Value = winword.exe Key = txt, Value = notepad.exe Value = paint.exe Value = paint.exe Value = winword.exe Value = hypertrm.exe Value = winword.exe Value = notepad.exe Indexed retrieval using the Values property: Values[2] = winword.exe Key = bmp Key = dib Key = doc Key = ht Key = rtf Key = txt Indexed retrieval using the Keys property: Keys[2] = doc Remove("doc") Key "doc" is not found. */
6. Dictionary<TKey,TValue> 字典集合
HashTable
HashTable 哈唏表, 也叫散列表,有关详细的Hash解说,请查看文章: Hash(散列函数)_百度百科 (baidu.com)
值得强调的是:常见的Hash算法有MD5(彩虹表,Hash撞库), SHA1 均已被破解,目前推荐的Hash 算法是:SHA2-256。
彩虹表: 用来存放所有hash值的部分hash值字典。然后通过碰撞破解密码
using System; using System.Collections; class Example { public static void Main() { Hashtable openWith = new Hashtable(); // 初始化一批数据,不可出现重复键 openWith.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); openWith.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("dib", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); // 如果出现重复键,则会抛出异常 try { openWith.Add("txt", "winword.exe"); } catch { Console.WriteLine("An element with Key = "txt" already exists."); } // 通过索引访问 Console.WriteLine("For key = "rtf", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // 修改索引所关联的值 openWith["rtf"] = "winword.exe"; Console.WriteLine("For key = "rtf", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // 给一个不存在的键赋值,则会新增 openWith["doc"] = "winword.exe"; // 判断是否包含 if (!openWith.ContainsKey("ht")) { openWith.Add("ht", "hypertrm.exe"); Console.WriteLine("Value added for key = "ht": {0}", openWith["ht"]); } // 遍历循环,元素被检索为 DictionaryEntry 对象 Console.WriteLine(); foreach( DictionaryEntry de in openWith ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}, Value = {1}", de.Key, de.Value); } // 获取所有的值集合 ICollection valueColl = openWith.Values; // 遍历值集合 Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in valueColl ) { Console.WriteLine("Value = {0}", s); } // 获取所有的键 ICollection keyColl = openWith.Keys; // 遍历键集合 Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in keyColl ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}", s); } // 移除键值对 Console.WriteLine("nRemove("doc")"); openWith.Remove("doc"); if (!openWith.ContainsKey("doc")) { Console.WriteLine("Key "doc" is not found."); } } }
不建议将类用于
Hashtable新开发。 相反,我们建议使用泛型 Dictionary 类。 有关详细信息,请参阅不应在GitHub上使用非泛型集合。
Dictionary<TKey,TValue>
表示键和值的集合。
-
TKey : 字典中的键的类型。
-
TValue : 字典中的值的类型。
Dictionary<string, string> openWith = new Dictionary<string, string>(); // 初始化数据,不能存在重复键 openWith.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); openWith.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("dib", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); // 添加重复键会抛出异常 try { openWith.Add("txt", "winword.exe"); } catch (ArgumentException) { Console.WriteLine("An element with Key = "txt" already exists."); } // 通过索引取值 Console.WriteLine("For key = "rtf", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // 给已存在的键值索引赋值 openWith["rtf"] = "winword.exe"; Console.WriteLine("For key = "rtf", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // 如果不存在,则会新增 openWith["doc"] = "winword.exe"; // 如果访问一个不存在的索引值,则会抛出异常 try { Console.WriteLine("For key = "tif", value = {0}.", openWith["tif"]); } catch (KeyNotFoundException) { Console.WriteLine("Key = "tif" is not found."); } // tryValue 尝试取值 string value = ""; if (openWith.TryGetValue("tif", out value)) { Console.WriteLine("For key = "tif", value = {0}.", value); } else { Console.WriteLine("Key = "tif" is not found."); } // 判断是否包含键 if (!openWith.ContainsKey("ht")) { openWith.Add("ht", "hypertrm.exe"); Console.WriteLine("Value added for key = "ht": {0}", openWith["ht"]); } // 遍历循环,元素被检索为 KeyValuePair 对象 Console.WriteLine(); foreach( KeyValuePair<string, string> kvp in openWith ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}, Value = {1}", kvp.Key, kvp.Value); } // 获取所有的值集合 Dictionary<string, string>.ValueCollection valueColl = openWith.Values; // 遍历值集合 Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in valueColl ) { Console.WriteLine("Value = {0}", s); } // 获取所有的键集合 Dictionary<string, string>.KeyCollection keyColl = openWith.Keys; // 遍历键集合 Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in keyColl ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}", s); } // 移除键值对 Console.WriteLine("nRemove("doc")"); openWith.Remove("doc"); if (!openWith.ContainsKey("doc")) { Console.WriteLine("Key "doc" is not found."); }
Dictionary泛型类提供从一组键到一组值的映射。 每次对字典的添加都包含一个值和与其关联的键。 通过使用其键检索值的速度非常快,接近 O (1) ,因为类 Dictionary 作为哈希表实现。
备注
检索速度取决于为
TKey类型指定的哈希算法的质量。
只要对象用作键, Dictionary它就不能以任何方式更改影响其哈希值。 每个键 Dictionary 都必须根据字典的相等比较器是唯一的。 如果键的类型是引用类型TValue,则键不能null,但值可以是。
Dictionary 需要相等实现来确定键是否相等。 可以使用接受comparer参数的构造函数指定泛型接口的IEqualityComparer实现;如果未指定实现,则使用默认泛型相等比较器EqualityComparer.Default。 如果类型 TKey 实现 System.IEquatable 泛型接口,则默认相等比较器使用该实现。
备注
例如,可以使用类提供的 StringComparer 不区分大小写的字符串比较器创建不区分大小写的字符串键的字典。
a Dictionary 的容量是可以保留的元素 Dictionary 数。 随着元素添加到 a Dictionary,通过重新分配内部数组,容量会自动增加。
线程安全性
只要集合未修改,A Dictionary 就可以同时支持多个读取器。 即便如此,通过集合进行遍历本质上不是线程安全的过程。 在遍历与写入访问竞争的极少数情况下,必须在整个遍历期间锁定集合。 若要允许多个线程访问集合以进行读写操作,则必须实现自己的同步。
有关线程安全的替代,请参阅 ConcurrentDictionary 类或 ImmutableDictionary 类。
7. ConcurrentDictionary 线程安全
表示可由多个线程同时访问的键/值对的线程安全集合。
-
TKey : 字典中的键的类型。
-
TValue :字典中的值的类型。
所有公共成员和受保护成员 ConcurrentDictionary 都是线程安全的,并且可以从多个线程并发使用。 但是,通过重写(包括扩展方法) ConcurrentDictionary 之一访问的成员不能保证线程安全,并且可能需要由调用方同步。
System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary与类一样,ConcurrentDictionary实现IDictionary接口。 此外, ConcurrentDictionary 还提供了几种方法用于在字典中添加或更新键/值对,如下表所述。
| 要执行此操作 | 方法 | 使用注意事项 |
|---|---|---|
| 将新键添加到字典(如果字典中尚不存在) | TryAdd | 如果字典中当前不存在该键,此方法将添加指定的键/值对。 该方法返回 true 或 false 取决于是否添加了新对。 |
| 更新字典中现有键的值(如果该键具有特定值) | TryUpdate | 此方法检查密钥是否具有指定的值,如果具有指定值,则使用新值更新密钥。 它类似于 CompareExchange 该方法,只不过它用于字典元素。 |
| 无条件地将键/值对存储在字典中,并覆盖已存在的键的值 | 索引器的 setter: dictionary[key] = newValue |
|
| 将键/值对添加到字典,或者如果键已存在,请根据键的现有值更新键的值 | AddOrUpdate(TKey, Func, Func)-system-func((-0-1-1)))) - 或 - AddOrUpdate(TKey, TValue, Func))) | AddOrUpdate(TKey, Func, Func)-system-func((-0-1-1)))) 接受Key和两个委托。 如果字典中不存在Key,它将使用第一个委托;它接受Key并返回应为Key添加的值。 如果密钥存在,它将使用第二个委托;它接受键及其当前值,并返回应为键设置的新值。 AddOrUpdate(TKey, TValue, Func))) 接受密钥、要添加的值和更新委托。 这与上一个重载相同,只不过它不使用委托来添加密钥。 |
| 获取字典中键的值,将值添加到字典中,如果键不存在,则返回它 | GetOrAdd(TKey, TValue) - 或 - GetOrAdd(TKey, Func))) | 这些重载为字典中的键/值对提供延迟初始化,仅当它不存在时才添加值。 GetOrAdd(TKey, TValue) 如果键不存在,则采用要添加的值。 GetOrAdd(TKey, Func))) 获取一个委托,如果键不存在,将生成该值。 |
所有这些操作都是原子操作,对于类上 ConcurrentDictionary 所有其他操作都是线程安全的。 唯一的例外是接受委托的方法,即 AddOrUpdate和 GetOrAdd。 若要对字典进行修改和写入操作, ConcurrentDictionary 请使用细粒度锁定来确保线程安全。 (字典上的读取操作以无锁方式执行。) 但是,这些方法的委托在锁外部调用,以避免在锁下执行未知代码时可能出现的问题。 因此,这些委托执行的代码不受操作的原子性的约束。
8. 思考题
利用特性,反射,扩展方法等知识,将一个枚举的特性描述,通过扩展方法封装到Dictionary<int,string> 集合中。例如:
Dictionary<string, string> openWith = new Dictionary<string, string>(); // 初始化数据,不能存在重复键 openWith.Add("txt", "notepad.exe"); openWith.Add("bmp", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("dib", "paint.exe"); openWith.Add("rtf", "wordpad.exe"); // 添加重复键会抛出异常 try { openWith.Add("txt", "winword.exe"); } catch (ArgumentException) { Console.WriteLine("An element with Key = "txt" already exists."); } // 通过索引取值 Console.WriteLine("For key = "rtf", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // 给已存在的键值索引赋值 openWith["rtf"] = "winword.exe"; Console.WriteLine("For key = "rtf", value = {0}.", openWith["rtf"]); // 如果不存在,则会新增 openWith["doc"] = "winword.exe"; // 如果访问一个不存在的索引值,则会抛出异常 try { Console.WriteLine("For key = "tif", value = {0}.", openWith["tif"]); } catch (KeyNotFoundException) { Console.WriteLine("Key = "tif" is not found."); } // tryValue 尝试取值 string value = ""; if (openWith.TryGetValue("tif", out value)) { Console.WriteLine("For key = "tif", value = {0}.", value); } else { Console.WriteLine("Key = "tif" is not found."); } // 判断是否包含键 if (!openWith.ContainsKey("ht")) { openWith.Add("ht", "hypertrm.exe"); Console.WriteLine("Value added for key = "ht": {0}", openWith["ht"]); } // 遍历循环,元素被检索为 KeyValuePair 对象 Console.WriteLine(); foreach( KeyValuePair<string, string> kvp in openWith ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}, Value = {1}", kvp.Key, kvp.Value); } // 获取所有的值集合 Dictionary<string, string>.ValueCollection valueColl = openWith.Values; // 遍历值集合 Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in valueColl ) { Console.WriteLine("Value = {0}", s); } // 获取所有的键集合 Dictionary<string, string>.KeyCollection keyColl = openWith.Keys; // 遍历键集合 Console.WriteLine(); foreach( string s in keyColl ) { Console.WriteLine("Key = {0}", s); } // 移除键值对 Console.WriteLine("nRemove("doc")"); openWith.Remove("doc"); if (!openWith.ContainsKey("doc")) { Console.WriteLine("Key "doc" is not found."); }
要求 封装OrderStateEnum的扩展 方法 ToDictionary() ,得到一个Dictionary<int,string>,效果如下
Dictionary<int,string> dict = OrderStateEnum.ToDictionary();




