- A+
所属分类:linux技术

链表只能一个一个的遍历,不能通过随机访问来获取节点

链表的地址是并要求连续的,是通过内部的指针来进行联系的

/******************************************************************************************************** * * * * * * * Copyright (c) 2023-2024 2556560122@qq.com All right Reserved * ******************************************************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdbool.h> // 指的是单向链表中的结点有效数据类型,用户可以根据需要进行修改 typedef int DataType_t; // 构造链表的结点,链表中所有结点的数据类型应该是相同的 typedef struct LinkedList { DataType_t data; // 结点的数据域 struct LinkedList *next; // 结点的指针域 } LList_t; // 创建一个空链表,空链表应该有一个头结点,对链表进行初始化 LList_t *LList_Create(void) { // 1.创建一个头结点并对头结点申请内存 LList_t *Head = (LList_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(LList_t)); if (NULL == Head) { perror("Calloc memory for Head is Failed"); exit(-1); } // 2.对头结点进行初始化,头结点是不存储有效内容的!!! Head->next = NULL; // 3.把头结点的地址返回即可 return Head; } // 创建新的结点,并对新结点进行初始化(数据域 + 指针域) LList_t *LList_NewNode(DataType_t data) { // 1.创建一个新结点并对新结点申请内存 LList_t *New = (LList_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(LList_t)); if (NULL == New) { perror("Calloc memory for NewNode is Failed"); return NULL; } // 2.对新结点的数据域和指针域进行初始化 New->data = data; New->next = NULL; return New; } // 头插 bool LList_HeadInsert(LList_t *Head, DataType_t data) { // 1.创建新的结点,并对新结点进行初始化 LList_t *New = LList_NewNode(data); if (NULL == New) { printf("can not insert new noden"); return false; } // 2.判断链表是否为空,如果为空,则直接插入即可 if (NULL == Head->next) { Head->next = New; return true; } // 3.如果链表为非空,则把新结点插入到链表的头部 New->next = Head->next; Head->next = New; return true; } // 尾插 bool LList_TailInsert(LList_t *Head, DataType_t data) { if (Head->next == NULL) { printf("链表尾空!n"); return false; } // 新建一个指针指向Head的next LList_t *copy_head = Head->next; // 创建一个新的节点 LList_t *newNode = LList_NewNode(data); while (copy_head) { // 到了尾节点了 if (copy_head->next == NULL) { // 尾插 copy_head->next = newNode; // 退出循环 break; } copy_head = copy_head->next; } return true; } // 插到目标节点的后面 bool LList_DestInsert(LList_t *Head, DataType_t dest, DataType_t data) { if (Head->next == NULL) { printf("链表尾空!n"); return false; } // 新建一个指针指向Head的next LList_t *copy_head = Head->next; // 创建一个新的节点 LList_t *newNode = LList_NewNode(data); while (copy_head) { // 找到了目标节点 if (copy_head->data == dest) { // 指向目标节点的next newNode->next = copy_head->next; // 目标节点指向新节点 copy_head->next = newNode; // 找到了,退出方法,放回true return true; } // 没找到,指针指向下个节点 copy_head = copy_head->next; } // 没找到 return false; } // 寻找链表的最小值 int Select_Min_Node(LList_t *Head) { if (Head->next == NULL) { printf("链表尾空!n"); return -1; } // 新建一个指针指向Head的next LList_t *copy_head = Head->next; // 默认最小值是copy_head的data int min = copy_head->data; while (copy_head->next) { // 如果min大于下个节点的数值,min就发生交换 if (min > copy_head->next->data) { min = copy_head->next->data; } // 进入下个节点 copy_head = copy_head->next; } return min; } // 删除最小数据的节点 void DelectMinDataNode(LList_t *Head) { if (Head->next == NULL) { printf("链表为空!n"); return; } // 新建一个指针指向Head的next LList_t *copy_head = Head; // 获取链表中的最小数据 int delVal = Select_Min_Node(Head); while (copy_head->next) { if (copy_head->next->data == delVal) { // 创建一个指针保存要删除的节点的next LList_t *copy_del_next = copy_head->next->next; // 释放空间 free(copy_head->next); // 指向要删除的节点的next copy_head->next = copy_del_next; // 退出循环 break; } copy_head = copy_head->next; } return; } // 遍历 void LList_Print(LList_t *Head) { // 对链表的头文件的地址进行备份 LList_t *Phead = Head; // 首结点 while (Phead->next) { // 把头的直接后继作为新的头结点 Phead = Phead->next; // 输出头结点的直接后继的数据域 printf("data = %dn", Phead->data); } } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { // 创建链表头节点 LList_t *Head = LList_Create(); // 头插 LList_HeadInsert(Head, 0); LList_HeadInsert(Head, 5); LList_HeadInsert(Head, 20); LList_HeadInsert(Head, 1); // 尾插 LList_TailInsert(Head, 20); // 在目标后面插 LList_DestInsert(Head, 5, 2); // 删除链表中数据最小的节点 DelectMinDataNode(Head); // 遍历链表 LList_Print(Head); return 0; } 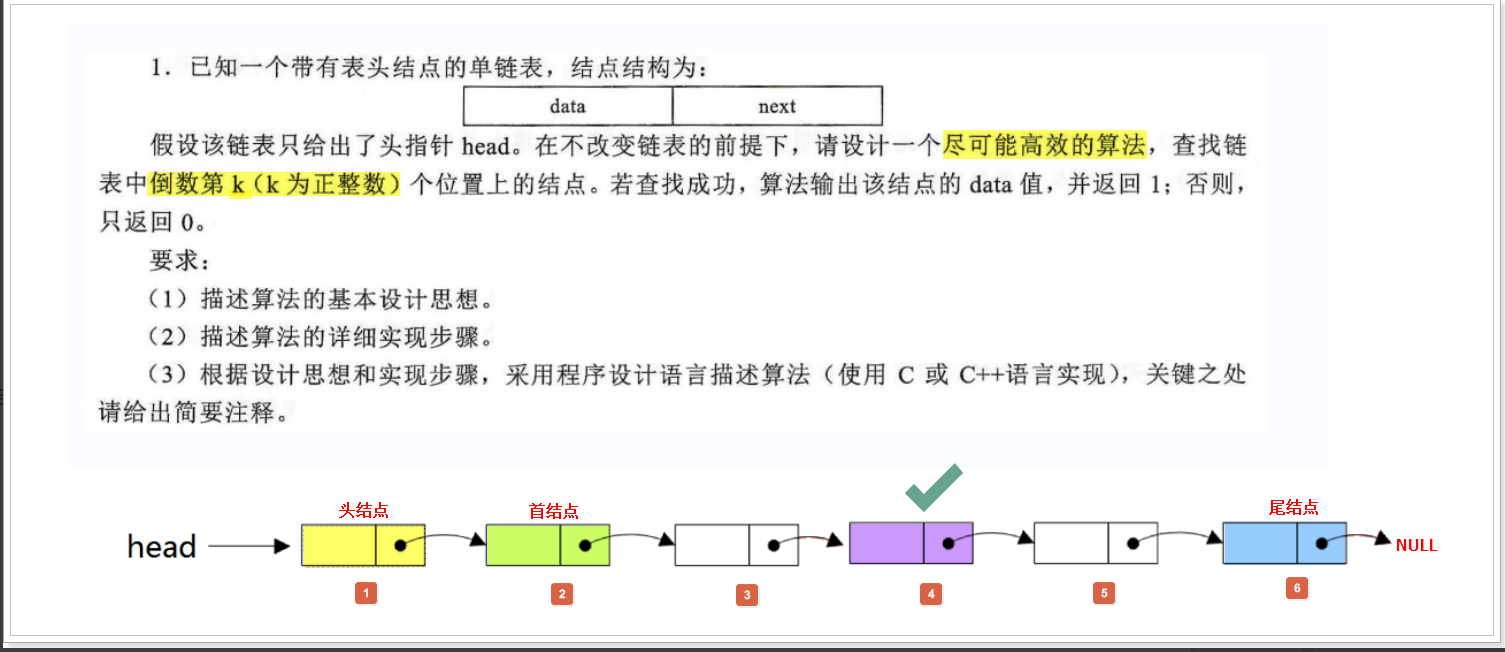
/******************************************************************************************************** * *查找链表的倒数第k个节点的数据 *思想: 可以根据链表的节点数-k来获取需要head的next的次数来获取节点 * * * * Copyright (c) 2023-2024 2556560122@qq.com All right Reserved * ******************************************************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdbool.h> // 指的是单向链表中的结点有效数据类型,用户可以根据需要进行修改 typedef int DataType_t; // 构造链表的结点,链表中所有结点的数据类型应该是相同的 typedef struct LinkedList { DataType_t data; // 结点的数据域 struct LinkedList *next; // 结点的指针域 } LList_t; // 创建一个空链表,空链表应该有一个头结点,对链表进行初始化 LList_t *LList_Create(void) { // 1.创建一个头结点并对头结点申请内存 LList_t *Head = (LList_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(LList_t)); if (NULL == Head) { perror("Calloc memory for Head is Failed"); exit(-1); } // 2.对头结点进行初始化,头结点是不存储有效内容的!!! Head->next = NULL; // 3.把头结点的地址返回即可 return Head; } // 创建新的结点,并对新结点进行初始化(数据域 + 指针域) LList_t *LList_NewNode(DataType_t data) { // 1.创建一个新结点并对新结点申请内存 LList_t *New = (LList_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(LList_t)); if (NULL == New) { perror("Calloc memory for NewNode is Failed"); return NULL; } // 2.对新结点的数据域和指针域进行初始化 New->data = data; New->next = NULL; return New; } // 头插 bool LList_HeadInsert(LList_t *Head, DataType_t data) { // 1.创建新的结点,并对新结点进行初始化 LList_t *New = LList_NewNode(data); if (NULL == New) { printf("can not insert new noden"); return false; } // 2.判断链表是否为空,如果为空,则直接插入即可 if (NULL == Head->next) { Head->next = New; return true; } // 3.如果链表为非空,则把新结点插入到链表的头部 New->next = Head->next; Head->next = New; return true; } // 遍历 void LList_Print(LList_t *Head) { // 对链表的头文件的地址进行备份 LList_t *Phead = Head; // 首结点 while (Phead->next) { // 把头的直接后继作为新的头结点 Phead = Phead->next; // 输出头结点的直接后继的数据域 printf("data = %dn", Phead->data); } } /******************************************************************************************************** * * 查找链表中倒数第k个位置上的节点 * ①先遍历链表记录链表的节点数 * ②然后通过for循环链表来获取到链表中倒数第k个位置上的节点,并且返回其data * ③找到返回1,没找到返回0 * * * * ******************************************************************************************************/ int SelectRecNode(LList_t *Head, DataType_t k) { if (Head->next == NULL) { printf("链表为空!n"); return 0; } // 新建一个指针指向Head的next LList_t *copy_head = Head->next; // 记录其节点数 int count = 0; // 通过while循环记录链表的节点数 while (copy_head) { count++; copy_head = copy_head->next; } // 把copy_head重新指向Head的next copy_head = Head->next; // 通过节点数-k就是其节点在链表中的位置 for (int i = 0; i < count - k; i++) { copy_head = copy_head->next; } printf("链表中倒数第%d个节点的数值是%dn", k, copy_head->data); return 1; } int main() { // 创建链表头节点 LList_t *Head = LList_Create(); // 头插 LList_HeadInsert(Head, 1); LList_HeadInsert(Head, 2); LList_HeadInsert(Head, 3); LList_HeadInsert(Head, 4); LList_HeadInsert(Head, 5); LList_HeadInsert(Head, 6); LList_Print(Head); SelectRecNode(Head, 3); } 



