- A+
中间件是一种装配到应用管道以处理请求和响应的软件。每个组件:
1、选择是否将请求传递到管道中的下一个组件。
2、可在管道中的下一个组件前后执行工作。
请求委托用于生成请求管道。请求委托处理每个 HTTP 请求。
请求管道中的每个中间件组件负责调用管道中的下一个组件,或使管道短路。当中间件短路时,它被称为“终端中间件”,因为它阻止中间件进一步处理请求。
废话不多说,我们直接来看一个Demo,Demo的目录结构如下所示:
本Demo的Web项目为ASP.NET Core Web 应用程序(目标框架为.NET Core 3.1) MVC项目。
其中 Home 控制器代码如下:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace NETCoreMiddleware.Controllers { public class HomeController : Controller { private readonly ILogger<HomeController> _logger; public HomeController(ILogger<HomeController> logger) { _logger = logger; } public IActionResult Index() { Console.WriteLine(""); Console.WriteLine($"This is {typeof(HomeController)} Index"); Console.WriteLine(""); return View(); } } }
其中 Startup.cs 类的代码如下:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace NETCoreMiddleware { public class Startup { public Startup(IConfiguration configuration) { Configuration = configuration; } public IConfiguration Configuration { get; } //服务注册(往容器中添加服务) // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container. public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddControllersWithViews(); } /// <summary> /// 配置Http请求处理管道 /// Http请求管道模型---就是Http请求被处理的步骤 /// 所谓管道,就是拿着HttpContext,经过多个步骤的加工,生成Response,这就是管道 /// </summary> /// <param name="app"></param> /// <param name="env"></param> // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) { #region 环境参数 if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } else { app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error"); } #endregion 环境参数 //静态文件中间件 app.UseStaticFiles(); #region Use中间件 //中间件1 app.Use(next => { Console.WriteLine("middleware 1"); return async context => { await Task.Run(() => { Console.WriteLine(""); Console.WriteLine("===================================Middleware==================================="); Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 1 Start"); }); await next.Invoke(context); await Task.Run(() => { Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 1 End"); Console.WriteLine("===================================Middleware==================================="); }); }; }); //中间件2 app.Use(next => { Console.WriteLine("middleware 2"); return async context => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 2 Start")); await next.Invoke(context); //可通过不调用 next 参数使请求管道短路 await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 2 End")); }; }); //中间件3 app.Use(next => { Console.WriteLine("middleware 3"); return async context => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 3 Start")); await next.Invoke(context); await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 3 End")); }; }); #endregion Use中间件 #region 最终把请求交给MVC app.UseRouting(); app.UseAuthorization(); app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllerRoute( name: "areas", pattern: "{area:exists}/{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); endpoints.MapControllerRoute( name: "default", pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); }); #endregion 最终把请求交给MVC } } }
用 Use 将多个请求委托链接在一起,next 参数表示管道中的下一个委托(下一个中间件)。
下面我们使用命令行(CLI)方式启动我们的网站,如下所示:
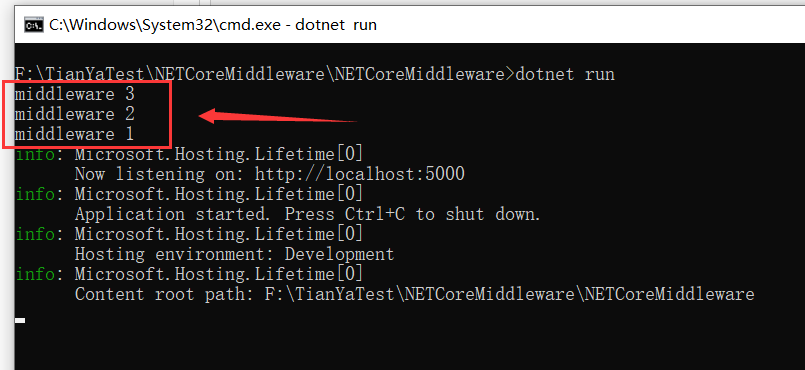
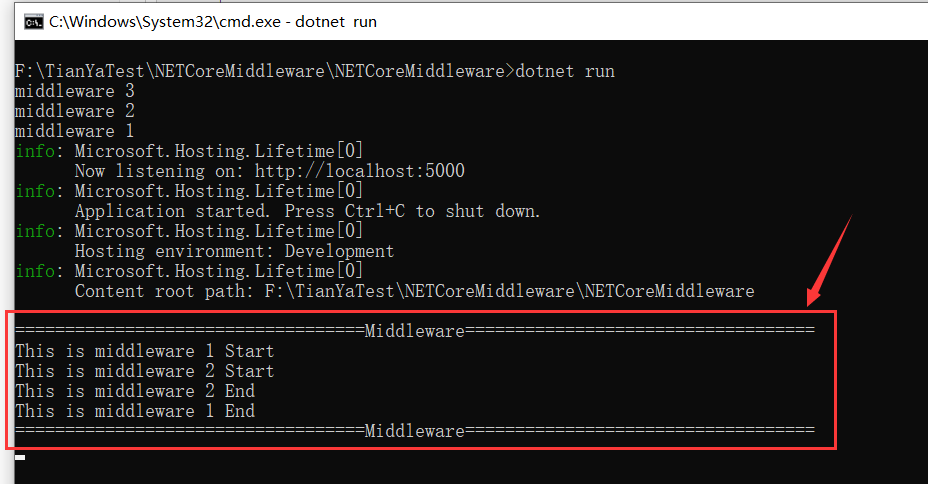
可以发现控制台依次输出了“middleware 3” 、“middleware 2”、“middleware 1”,这是怎么回事呢?此处我们先留个疑问,该点在后面的讲解中会再次提到。
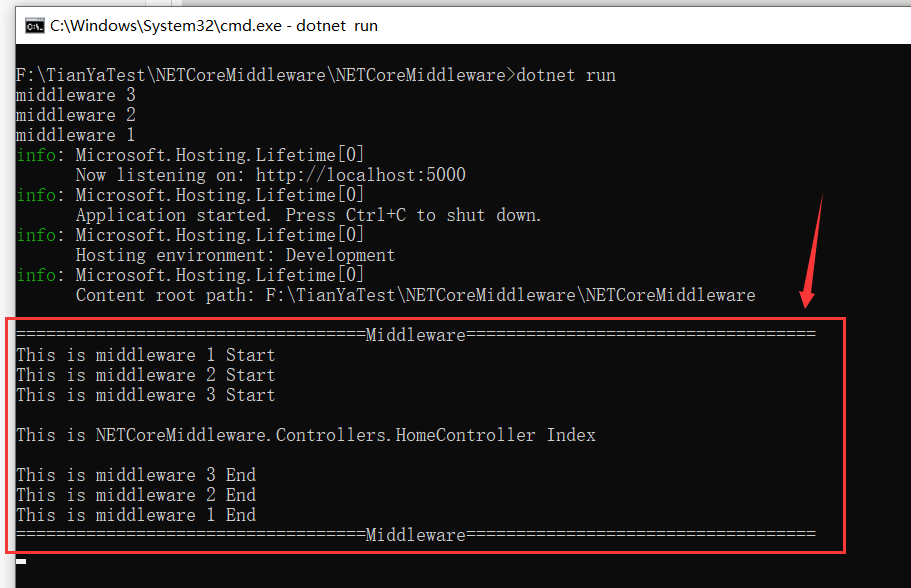
启动成功后,我们来访问一下 “/home/index” ,控制台输出结果如下所示:
请求管道包含一系列请求委托,依次调用,下图演示了这一过程:
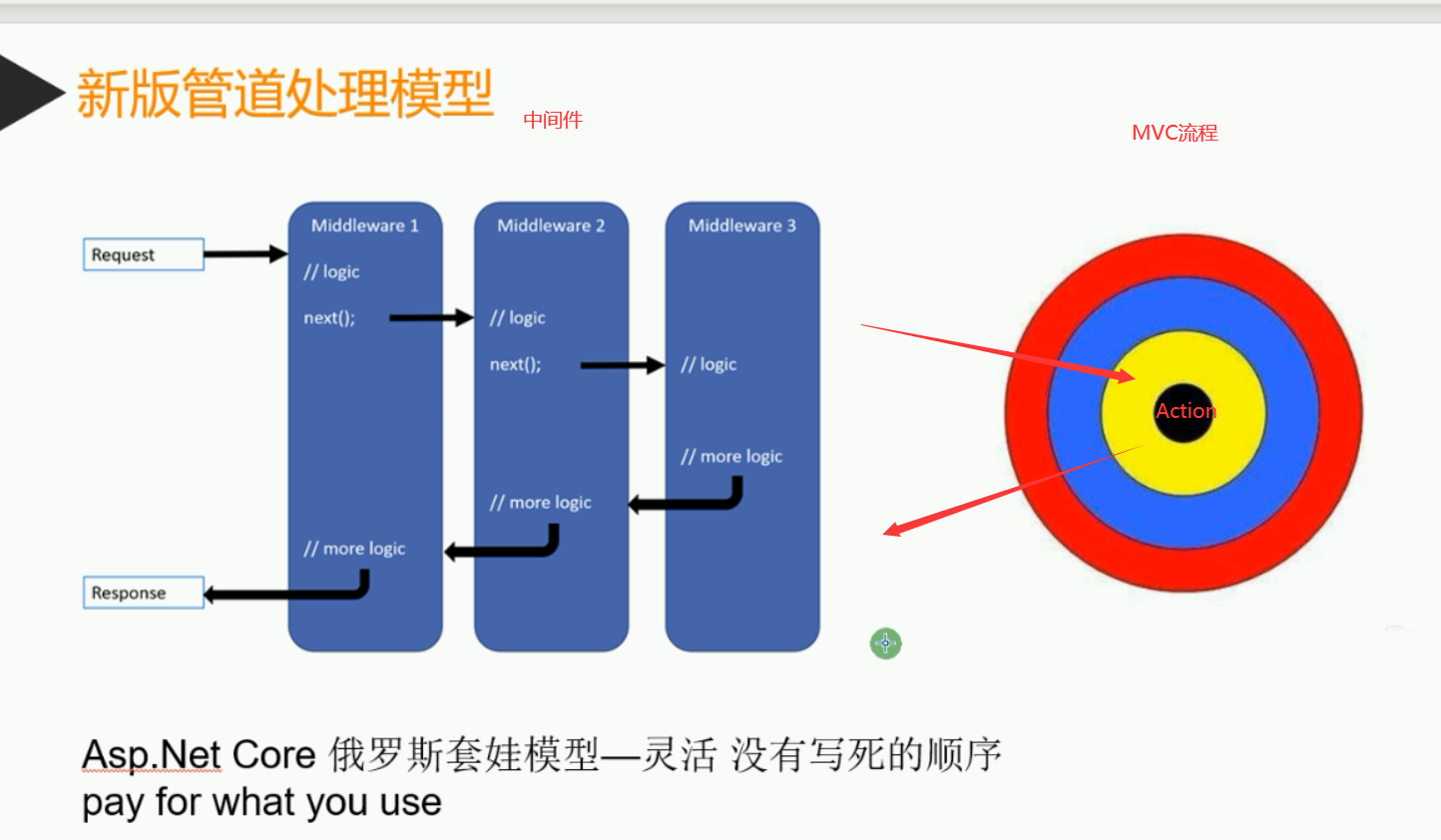
每个委托均可在下一个委托前后执行操作。应尽早在管道中调用异常处理委托,这样它们就能捕获在管道的后期阶段发生的异常。
此外,可通过不调用 next 参数使请求管道短路,如下所示:
/// <summary> /// 配置Http请求处理管道 /// Http请求管道模型---就是Http请求被处理的步骤 /// 所谓管道,就是拿着HttpContext,经过多个步骤的加工,生成Response,这就是管道 /// </summary> /// <param name="app"></param> /// <param name="env"></param> // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) { #region 环境参数 if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } else { app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error"); } #endregion 环境参数 //静态文件中间件 app.UseStaticFiles(); #region Use中间件 //中间件1 app.Use(next => { Console.WriteLine("middleware 1"); return async context => { await Task.Run(() => { Console.WriteLine(""); Console.WriteLine("===================================Middleware==================================="); Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 1 Start"); }); await next.Invoke(context); await Task.Run(() => { Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 1 End"); Console.WriteLine("===================================Middleware==================================="); }); }; }); //中间件2 app.Use(next => { Console.WriteLine("middleware 2"); return async context => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 2 Start")); //await next.Invoke(context); //可通过不调用 next 参数使请求管道短路 await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 2 End")); }; }); //中间件3 app.Use(next => { Console.WriteLine("middleware 3"); return async context => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 3 Start")); await next.Invoke(context); await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 3 End")); }; }); #endregion Use中间件 #region 最终把请求交给MVC app.UseRouting(); app.UseAuthorization(); app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllerRoute( name: "areas", pattern: "{area:exists}/{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); endpoints.MapControllerRoute( name: "default", pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); }); #endregion 最终把请求交给MVC }
此处我们注释掉了 中间件2 的 next 参数调用,使请求管道短路。下面我们重新编译后再次访问 “/home/index” ,控制台输出结果如下所示:
当委托不将请求传递给下一个委托时,它被称为“让请求管道短路”。 通常需要短路,因为这样可以避免不必要的工作。 例如,静态文件中间件可以处理对静态文件的请求,并让管道的其余部分短路,从而起到终端中间件的作用。
对于终端中间件,框架专门为我们提供了一个叫 app.Run(...) 的扩展方法,其实该方法的内部也是调用 app.Use(...) 这个方法的,下面我们来看个示例:
/// <summary> /// 配置Http请求处理管道 /// Http请求管道模型---就是Http请求被处理的步骤 /// 所谓管道,就是拿着HttpContext,经过多个步骤的加工,生成Response,这就是管道 /// </summary> /// <param name="app"></param> /// <param name="env"></param> // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) { #region 环境参数 if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } else { app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error"); } #endregion 环境参数 //静态文件中间件 app.UseStaticFiles(); #region Use中间件 //中间件1 app.Use(next => { Console.WriteLine("middleware 1"); return async context => { await Task.Run(() => { Console.WriteLine(""); Console.WriteLine("===================================Middleware==================================="); Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 1 Start"); }); await next.Invoke(context); await Task.Run(() => { Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 1 End"); Console.WriteLine("===================================Middleware==================================="); }); }; }); //中间件2 app.Use(next => { Console.WriteLine("middleware 2"); return async context => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 2 Start")); await next.Invoke(context); //可通过不调用 next 参数使请求管道短路 await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 2 End")); }; }); //中间件3 app.Use(next => { Console.WriteLine("middleware 3"); return async context => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 3 Start")); await next.Invoke(context); await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 3 End")); }; }); #endregion Use中间件 #region 终端中间件 //app.Use(_ => handler); app.Run(async context => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is Run")); }); #endregion 终端中间件 #region 最终把请求交给MVC app.UseRouting(); app.UseAuthorization(); app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllerRoute( name: "areas", pattern: "{area:exists}/{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); endpoints.MapControllerRoute( name: "default", pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); }); #endregion 最终把请求交给MVC }
Run 委托不会收到 next 参数。第一个 Run 委托始终为终端,用于终止管道。Run 是一种约定。某些中间件组件可能会公开在管道末尾运行 Run[Middleware] 方法。
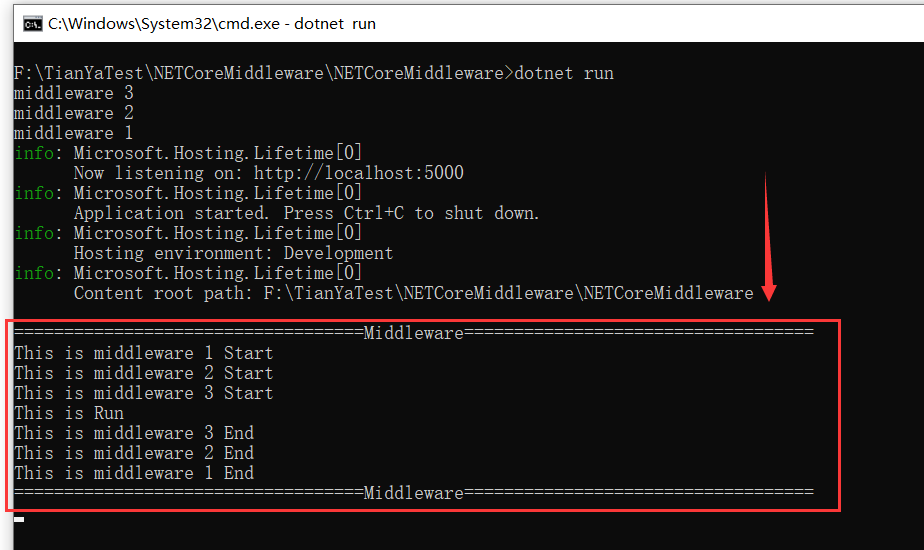
我们重新编译后再次访问 “/home/index” ,控制台输出结果如下所示:
此外,app.Use(...) 方法还有另外一个重载,如下所示(中间件4):
/// <summary> /// 配置Http请求处理管道 /// Http请求管道模型---就是Http请求被处理的步骤 /// 所谓管道,就是拿着HttpContext,经过多个步骤的加工,生成Response,这就是管道 /// </summary> /// <param name="app"></param> /// <param name="env"></param> // This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) { #region 环境参数 if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } else { app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error"); } #endregion 环境参数 //静态文件中间件 app.UseStaticFiles(); #region Use中间件 //中间件1 app.Use(next => { Console.WriteLine("middleware 1"); return async context => { await Task.Run(() => { Console.WriteLine(""); Console.WriteLine("===================================Middleware==================================="); Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 1 Start"); }); await next.Invoke(context); await Task.Run(() => { Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 1 End"); Console.WriteLine("===================================Middleware==================================="); }); }; }); //中间件2 app.Use(next => { Console.WriteLine("middleware 2"); return async context => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 2 Start")); await next.Invoke(context); //可通过不调用 next 参数使请求管道短路 await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 2 End")); }; }); //中间件3 app.Use(next => { Console.WriteLine("middleware 3"); return async context => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 3 Start")); await next.Invoke(context); await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 3 End")); }; }); //中间件4 //Use方法的另外一个重载 app.Use(async (context, next) => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 4 Start")); await next(); await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 4 End")); }); #endregion Use中间件 #region 终端中间件 //app.Use(_ => handler); app.Run(async context => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is Run")); }); #endregion 终端中间件 #region 最终把请求交给MVC app.UseRouting(); app.UseAuthorization(); app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllerRoute( name: "areas", pattern: "{area:exists}/{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); endpoints.MapControllerRoute( name: "default", pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); }); #endregion 最终把请求交给MVC }
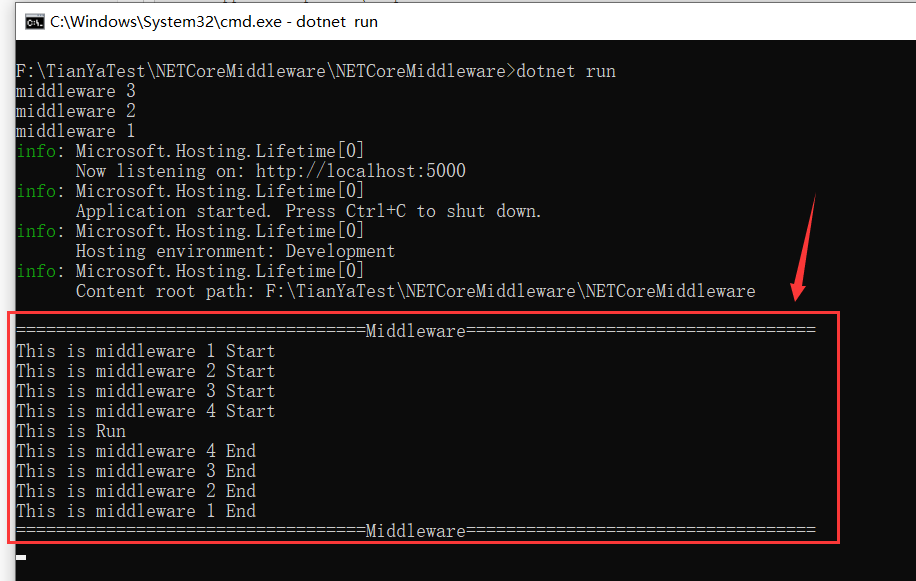
我们重新编译后再次访问 “/home/index” ,控制台输出结果如下所示:
下面我们结合ASP.NET Core源码来分析下其实现原理:
首先我们通过调试来看下 IApplicationBuilder 的实现类到底是啥?如下所示:
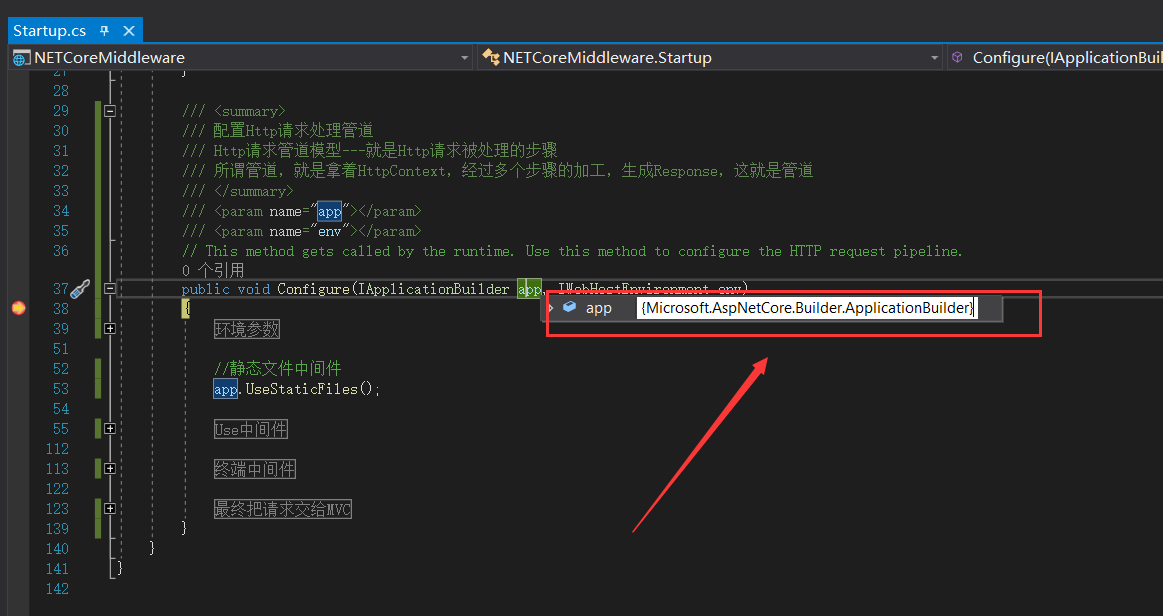
可以看出它的实现类是 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder.ApplicationBuilder ,我们找到 ApplicationBuilder 类的源码,如下所示:
// Copyright (c) .NET Foundation. All rights reserved. // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See License.txt in the project root for license information. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Features; using Microsoft.Extensions.Internal; namespace Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder { public class ApplicationBuilder : IApplicationBuilder { private const string ServerFeaturesKey = "server.Features"; private const string ApplicationServicesKey = "application.Services"; private readonly IList<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>> _components = new List<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>(); public ApplicationBuilder(IServiceProvider serviceProvider) { Properties = new Dictionary<string, object>(StringComparer.Ordinal); ApplicationServices = serviceProvider; } public ApplicationBuilder(IServiceProvider serviceProvider, object server) : this(serviceProvider) { SetProperty(ServerFeaturesKey, server); } private ApplicationBuilder(ApplicationBuilder builder) { Properties = new CopyOnWriteDictionary<string, object>(builder.Properties, StringComparer.Ordinal); } public IServiceProvider ApplicationServices { get { return GetProperty<IServiceProvider>(ApplicationServicesKey); } set { SetProperty<IServiceProvider>(ApplicationServicesKey, value); } } public IFeatureCollection ServerFeatures { get { return GetProperty<IFeatureCollection>(ServerFeaturesKey); } } public IDictionary<string, object> Properties { get; } private T GetProperty<T>(string key) { object value; return Properties.TryGetValue(key, out value) ? (T)value : default(T); } private void SetProperty<T>(string key, T value) { Properties[key] = value; } public IApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware) { _components.Add(middleware); return this; } public IApplicationBuilder New() { return new ApplicationBuilder(this); } public RequestDelegate Build() { RequestDelegate app = context => { // If we reach the end of the pipeline, but we have an endpoint, then something unexpected has happened. // This could happen if user code sets an endpoint, but they forgot to add the UseEndpoint middleware. var endpoint = context.GetEndpoint(); var endpointRequestDelegate = endpoint?.RequestDelegate; if (endpointRequestDelegate != null) { var message = $"The request reached the end of the pipeline without executing the endpoint: '{endpoint.DisplayName}'. " + $"Please register the EndpointMiddleware using '{nameof(IApplicationBuilder)}.UseEndpoints(...)' if using " + $"routing."; throw new InvalidOperationException(message); } context.Response.StatusCode = 404; return Task.CompletedTask; }; foreach (var component in _components.Reverse()) { app = component(app); } return app; } } }
其中 RequestDelegate 委托的声明,如下:
// Copyright (c) .NET Foundation. All rights reserved. // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See License.txt in the project root for license information. using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http { /// <summary> /// A function that can process an HTTP request. /// </summary> /// <param name="context">The <see cref="HttpContext"/> for the request.</param> /// <returns>A task that represents the completion of request processing.</returns> public delegate Task RequestDelegate(HttpContext context); }
仔细阅读后可以发现其实 app.Use(...) 这个方法就只是将 Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> 类型的委托参数添加到 _components 这个集合中。
最终程序会调用 ApplicationBuilder 类的 Build() 方法去构建Http请求处理管道,接下来我们就重点来关注一下这个 Build() 方法,如下:
public RequestDelegate Build() { RequestDelegate app = context => { // If we reach the end of the pipeline, but we have an endpoint, then something unexpected has happened. // This could happen if user code sets an endpoint, but they forgot to add the UseEndpoint middleware. var endpoint = context.GetEndpoint(); var endpointRequestDelegate = endpoint?.RequestDelegate; if (endpointRequestDelegate != null) { var message = $"The request reached the end of the pipeline without executing the endpoint: '{endpoint.DisplayName}'. " + $"Please register the EndpointMiddleware using '{nameof(IApplicationBuilder)}.UseEndpoints(...)' if using " + $"routing."; throw new InvalidOperationException(message); } context.Response.StatusCode = 404; return Task.CompletedTask; }; foreach (var component in _components.Reverse()) { app = component(app); } return app; }
仔细观察上面的源码后我们可以发现:
1、首先它是将 _components 这个集合反转(即:_components.Reverse()),然后依次调用里面的中间件(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>委托),这也就解释了为什么网站启动时我们的控制台会依次输出 “middleware 3” 、“middleware 2”、“middleware 1” 的原因。
2、调用反转后的第一个中间件(即:注册的最后一个中间件)时传入的参数是状态码为404的 RequestDelegate 委托,作为默认处理步骤。
3、在调用反转后的中间件时,它是用第一个中间件的返回值作为调用第二个中间件的参数,用第二个中间件的返回值作为调用第三个中间件的参数,依次类推。这也就是为什么说注册时的那个 next 参数是指向注册时下一个中间件的原因。
4、Build() 方法最终返回的是调用反转后最后一个中间件(即:注册的第一个中间件)的返回值。
下面我们来看一下Use方法的另外一个重载,如下所示:
//中间件4 //Use方法的另外一个重载 app.Use(async (context, next) => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 4 Start")); await next(); await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is middleware 4 End")); });
我们找到它的源码,如下:
// Copyright (c) .NET Foundation. All rights reserved. // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See License.txt in the project root for license information. using System; using System.Threading.Tasks; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; namespace Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder { /// <summary> /// Extension methods for adding middleware. /// </summary> public static class UseExtensions { /// <summary> /// Adds a middleware delegate defined in-line to the application's request pipeline. /// </summary> /// <param name="app">The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</param> /// <param name="middleware">A function that handles the request or calls the given next function.</param> /// <returns>The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</returns> public static IApplicationBuilder Use(this IApplicationBuilder app, Func<HttpContext, Func<Task>, Task> middleware) { return app.Use(next => { return context => { Func<Task> simpleNext = () => next(context); return middleware(context, simpleNext); }; }); } } }
可以发现其实它是个扩展方法,主要就是对 app.Use(...) 这个方法包装了一下,最终调用的还是 app.Use(...) 这个方法。
最后我们来看一下 app.Run(...) 这个扩展方法,如下所示:
//app.Use(_ => handler); app.Run(async context => { await Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine($"This is Run")); });
我们找到它的源码,如下:
// Copyright (c) .NET Foundation. All rights reserved. // Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See License.txt in the project root for license information. using System; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; namespace Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder { /// <summary> /// Extension methods for adding terminal middleware. /// </summary> public static class RunExtensions { /// <summary> /// Adds a terminal middleware delegate to the application's request pipeline. /// </summary> /// <param name="app">The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</param> /// <param name="handler">A delegate that handles the request.</param> public static void Run(this IApplicationBuilder app, RequestDelegate handler) { if (app == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(app)); } if (handler == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(handler)); } app.Use(_ => handler); } } }
可以发现,其实 app.Run(...) 这个扩展方法最终也是调用 app.Use(...) 这个方法,只不过它直接丢弃了 next 参数,故调用这个方法会终止管道,它属于终端中间件。
更多关于ASP.NET Core 中间件的相关知识可参考微软官方文档: https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/fundamentals/middleware/?view=aspnetcore-6.0
至此本文就全部介绍完了,如果觉得对您有所启发请记得点个赞哦!!!
Demo源码:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/103ldhtjVcB3vJZidlcq0Yw 提取码:7rt1
此文由博主精心撰写转载请保留此原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xyh9039/p/16146620.html
版权声明:如有雷同纯属巧合,如有侵权请及时联系本人修改,谢谢!!!




